Events on the Kursk Bulge. The Battle of Kursk is a radical turning point in the Great Patriotic War and World War II. Offensive operation "Rumyantsev"
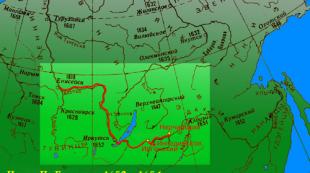
During the winter offensive of the Red Army and the subsequent counter-offensive of the Wehrmacht in Eastern Ukraine, a ledge up to 150 km deep and up to 200 km wide was formed in the center of the Soviet-German front, facing the west (the so-called "Kursk Bulge"). During April-June, there was an operational pause at the front, during which the parties were preparing for the summer campaign.
Plans and forces of the parties
The German command decided to conduct a major strategic operation on the Kursk ledge in the summer of 1943. It was planned to launch converging strikes from the areas of the cities of Orel (from the north) and Belgorod (from the south). The shock groups were to link up in the Kursk region, surrounding the troops of the Central and Voronezh Fronts of the Red Army. The operation received the code name "Citadel". At a meeting with Manstein on May 10-11, the plan was adjusted at the suggestion of Gott: the 2nd such SS corps turns from the Oboyansky direction towards Prokhorovka, where terrain conditions allow for a global battle with the armored reserves of Soviet troops. And, based on the losses, continue the offensive or go on the defensive. (From the interrogation of the chief of staff of the 4th tank army, General Fangor)
Kursk defensive operation
The German offensive began on the morning of July 5, 1943. Since the Soviet command knew exactly the start time of the operation - 3 a.m. (the German army fought according to Berlin time - translated into Moscow 5 a.m.), at 22:30 and 2:20 Moscow time, counter-barrage preparation was carried out by the forces of two fronts with the amount of ammunition 0.25 ammo. German reports noted significant damage to communication lines and minor losses in manpower. An unsuccessful air raid was also carried out by the forces of the 2nd and 17th air armies (more than 400 attack aircraft and fighters) on the Kharkov and Belgorod enemy air hubs.
Battle of Prokhorovka
On July 12, the largest oncoming tank battle in history took place in the Prokhorovka area. From the German side, according to V. Zamulin, the 2nd SS Panzer Corps participated in it, which had 494 tanks and self-propelled guns, including 15 Tigers and not a single Panther. According to Soviet sources, about 700 tanks and assault guns participated in the battle from the German side. On the Soviet side, the 5th Panzer Army of P. Rotmistrov, numbering about 850 tanks, participated in the battle. After a massive air strike [source not specified 237 days], the battle on both sides entered its active phase and continued until the end of the day. By the end of July 12, the battle ended with unclear results, only to resume on the afternoon of July 13 and 14. After the battle, the German troops could not move forward in any significant way, despite the fact that the losses of the Soviet tank army, caused by tactical errors of its command, were much greater. Having advanced 35 kilometers over July 5-12, Manstein's troops were forced, having trampled on the achieved lines for three days in vain attempts to break into the Soviet defenses, to begin the withdrawal of troops from the captured "bridgehead". During the battle there was a turning point. The Soviet troops, which went on the offensive on July 23, threw back the German armies in the south of the Kursk Bulge to their original positions.
Losses
According to Soviet data, about 400 German tanks, 300 vehicles, over 3,500 soldiers and officers remained on the battlefield in the battle of Prokhorovka. However, these numbers are being questioned. For example, according to the calculations of G. A. Oleinikov, more than 300 German tanks could not take part in the battle. According to the research of A. Tomzov, referring to the data of the German Federal Military Archive, during the battles of July 12-13, the Leibstandarte Adolf Hitler division irretrievably lost 2 Pz.IV tanks, 2 Pz.IV and 2 Pz.III tanks were sent for long-term repairs , in the short term - 15 Pz.IV and 1 Pz.III tanks. The total losses of tanks and assault guns of the 2nd SS TC on July 12 amounted to about 80 tanks and assault guns, including at least 40 units lost by the Totenkopf Division.
- At the same time, the Soviet 18th and 29th tank corps of the 5th Guards Tank Army lost up to 70% of their tanks
The central front involved in the battle in the north of the arc, for July 5-11, 1943, suffered losses of 33,897 people, of which 15,336 were irretrievable, its enemy, the 9th Army of the Model, lost 20,720 people over the same period, which gives a loss ratio of 1.64:1. The Voronezh and Steppe fronts, which participated in the battle on the southern face of the arc, lost 143,950 people on July 5-23, 1943, according to modern official estimates (2002), of which 54,996 were irrevocable. Including only the Voronezh Front - 73,892 total losses. However, the chief of staff of the Voronezh Front, Lieutenant General Ivanov, and the head of the operational department of the front headquarters, Major General Teteshkin, thought differently: they believed the losses of their front to be 100,932 people, of which 46,500 were irretrievable. If, contrary to Soviet documents of the war period, the official numbers are considered correct, then taking into account German losses on the southern front of 29,102 people, the ratio of the losses of the Soviet and German sides is 4.95: 1 here.
- For the period from July 5 to 12, 1943, the Central Front used up 1079 wagons of ammunition, and the Voronezh - 417 wagons, almost two and a half times less.
Results of the defensive phase of the battle
The reason that the losses of the Voronezh Front so sharply exceeded the losses of the Central Front was the smaller massing of forces and means in the direction of the German attack, which allowed the Germans to actually achieve an operational breakthrough on the southern face of the Kursk salient. Although the breakthrough was closed by the forces of the Steppe Front, it allowed the attackers to achieve favorable tactical conditions for their troops. It should be noted that only the absence of homogeneous independent tank formations did not give the German command the opportunity to concentrate their armored forces in the direction of the breakthrough and develop it in depth.
Oryol offensive operation (Operation Kutuzov). On July 12, the Western (commanded by Colonel General Vasily Sokolovsky) and Bryansk (commanded by Colonel General Markian Popov) fronts launched an offensive against the 2nd Panzer and 9th armies of the enemy in the Orel region. By the end of the day on July 13, Soviet troops broke through the enemy defenses. On July 26, the Germans left the Orlovsky bridgehead and began to withdraw to the Hagen defensive line (east of Bryansk). On August 5, at 05-45, Soviet troops completely liberated Oryol.
Belgorod-Kharkov offensive operation (Operation Rumyantsev). On the southern front, the counteroffensive by the forces of the Voronezh and Steppe fronts began on August 3. On August 5, at about 18-00, Belgorod was liberated, on August 7 - Bogodukhov. Developing the offensive, the Soviet troops cut the Kharkov-Poltava railroad on August 11, and captured Kharkov on August 23. The German counterattacks were not successful.
- On August 5, the first salute in the entire war was given in Moscow - in honor of the liberation of Orel and Belgorod.
Results of the Battle of Kursk
- The victory near Kursk marked the transition of the strategic initiative to the Red Army. By the time the front was stabilized, Soviet troops had reached their starting positions for an offensive on the Dnieper.
- After the end of the battle on the Kursk Bulge, the German command lost the opportunity to conduct strategic offensive operations. Local massive offensives, such as Watch on the Rhine (1944) or the Balaton operation (1945) were also not successful.
- Field Marshal Erich von Manstein, who developed and carried out Operation Citadel, later wrote:
- It was the last attempt to keep our initiative in the East. With her failure, tantamount to failure, the initiative finally passed to the Soviet side. Therefore, Operation Citadel is a decisive turning point in the war on the Eastern Front.
- - Manstein E. Lost victories. Per. with him. - M., 1957. - S. 423
- According to Guderian,
- As a result of the failure of the Citadel offensive, we suffered a decisive defeat. The armored forces, replenished with such great difficulty, were put out of action for a long time due to heavy losses in people and equipment.
- - Guderian G. Memoirs of a soldier. - Smolensk: Rusich, 1999
Differences in loss estimates
- The losses of the parties in the battle remain unclear. Thus, Soviet historians, including Academician of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR A. M. Samsonov, speak of more than 500,000 killed, wounded and captured, 1,500 tanks and over 3,700 aircraft.
However, German archival data show that in July-August 1943, the Wehrmacht lost 537,533 people on the entire Eastern Front. These figures include those killed, wounded, sick, missing (the number of German prisoners in this operation was insignificant). And even despite the fact that the main fighting at that time took place in the Kursk region, the Soviet figures for German losses of 500,000 look somewhat exaggerated.
- In addition, according to German documents, on the entire Eastern Front, the Luftwaffe lost 1696 aircraft in July-August 1943.
On the other hand, even Soviet commanders during the war years did not consider the Soviet military reports about German losses to be true. So, General Malinin (chief of staff of the front) wrote to the lower headquarters: “Looking through the daily results of the day on the amount of manpower and equipment destroyed and captured trophies, I came to the conclusion that these data are significantly overestimated and, therefore, do not correspond to reality.”
On August 23, Russia celebrates the Day of the defeat of the Nazi troops in the Battle of Kursk
In world history there are no analogues of the Battle of Kursk, which lasted 50 days and nights - from July 5 to August 23, 1943. The victory in the Battle of Kursk was a decisive turning point in the course of the Great Patriotic War. The defenders of our Motherland managed to stop the enemy and deal him a deafening blow, from which he could not recover. After the victory in the Battle of Kursk, the advantage in the Great Patriotic War was already on the side of the Soviet army. But such a radical change cost our country dearly: military historians still cannot accurately assess the losses of people and equipment on the Kursk Bulge, concurring in only one assessment - the losses of both sides were colossal.
According to the plan of the German command, the Soviet troops of the Central and Voronezh fronts defending in the Kursk region were to be destroyed as a result of a series of massive attacks. The victory in the Battle of Kursk gave the Germans the opportunity to expand their offensive plan against our country and their strategic initiative. In short, victory in this battle meant victory in the war. In the Battle of Kursk, the Germans had high hopes for their new equipment: Tiger and Panther tanks, Ferdinand assault guns, Focke-Wulf-190-A fighters and Heinkel-129 attack aircraft. Our attack aircraft used the new PTAB-2.5-1.5 anti-tank bombs, which pierced the armor of the fascist Tigers and Panthers.
The Kursk Bulge was a ledge about 150 kilometers deep and up to 200 kilometers wide, facing west. This arc was formed during the winter offensive of the Red Army and the subsequent counter-offensive of the Wehrmacht in Eastern Ukraine. The battle on the Kursk Bulge is usually divided into three parts: the Kursk defensive operation, which lasted from July 5 to 23, Oryol (July 12 - August 18) and Belgorod-Kharkov (August 3 - 23).
The German military operation to seize control of the strategically important Kursk Bulge was codenamed "Citadel". Avalanche-like attacks on Soviet positions began on the morning of July 5, 1943 with artillery fire and air strikes. The Nazis advanced on a broad front, attacking from heaven and earth. As soon as it began, the battle took on a grandiose scope and was of an extremely tense character. According to Soviet sources, the defenders of our Motherland were opposed by about 900 thousand people, up to 10 thousand guns and mortars, about 2.7 thousand tanks and more than 2 thousand aircraft. In addition, aces of the 4th and 6th air fleets fought in the air from the German side. The command of the Soviet troops managed to collect more than 1.9 million people, more than 26.5 thousand guns and mortars, over 4.9 thousand tanks and self-propelled artillery installations and about 2.9 thousand aircraft. Our soldiers repelled the attacks of the enemy's strike groups, showing unprecedented stamina and courage.
On July 12, Soviet troops on the Kursk Bulge went on the offensive. On this day, in the area of the Prokhorovka railway station, 56 km north of Belgorod, the largest oncoming tank battle of the Second World War took place. About 1,200 tanks and self-propelled guns took part in it. The battle of Prokhorovka lasted all day, the Germans lost about 10 thousand people, over 360 tanks and were forced to retreat. On the same day, Operation Kutuzov began, during which the enemy’s defenses were broken through in the Bolkhovsky, Khotynets and Oryol directions. Our troops advanced inside the German positions, and the enemy command gave the order to retreat. By August 23, the enemy was driven back 150 kilometers to the west, the cities of Orel, Belgorod and Kharkov were liberated.
Aviation played a significant role in the Battle of Kursk. Air strikes destroyed a significant amount of enemy equipment. The advantage of the USSR in the air, achieved in the course of fierce battles, became the key to the overall superiority of our troops. In the memoirs of the German military, admiration for the enemy and recognition of his strength are felt. The German General Forst wrote after the war: “Our offensive began, and a few hours later a large number of Russian aircraft appeared. Air battles broke out over our heads. During the entire war, none of us saw such a spectacle. A German fighter pilot from the Udet squadron, shot down on July 5 near Belgorod, recalls: “Russian pilots began to fight much harder. Looks like you have some old footage. I never thought that I would be shot down so soon…”
And about how fierce the battles were on the Kursk Bulge and about what inhuman efforts this victory was achieved, the memoirs of the battery commander of the 239th mortar regiment of the 17th artillery division M. I. Kobzev will best tell:
– The fierce battles on the Oryol-Kursk Bulge in August 1943 especially stuck in my memory,” Kobzev wrote. - It was in the Akhtyrka area. My battery was ordered to cover the withdrawal of our troops with mortar fire, blocking the way for the enemy infantry advancing behind the tanks. The calculations of my battery had a hard time when the Tigers began to pour a hail of fragments on it. They disabled two mortars and almost half of the servants. The loader was killed by a direct hit of the projectile, the enemy bullet hit the gunner's head, the chin of the third number was torn off by a fragment. Miraculously, only one battery mortar remained intact, disguised in corn thickets, which, together with a reconnaissance officer and a radio operator, dragged 17 kilometers together for two days until we found our regiment that had retreated to the given positions.
On August 5, 1943, when the Soviet army clearly had an advantage in the Battle of Kursk in Moscow, for the first time in 2 years since the beginning of the war, an artillery salute was fired in honor of the liberation of Orel and Belgorod. Subsequently, Muscovites often observed fireworks on the days of significant victories in the battles of the Great Patriotic War.
Vasily Klochkov
The battle on the Kursk Bulge lasted 50 days. As a result of this operation, the strategic initiative finally went over to the side of the Red Army and, until the end of the war, was carried out mainly in the form of offensive actions on its part. On the day of the 75th anniversary of the start of the legendary battle, the website of the Zvezda TV channel collected ten little-known facts about the Battle of Kursk. 1. Initially, the battle was not planned as an offensive When planning the spring-summer military campaign of 1943, the Soviet command faced a difficult choice: which method of action to prefer - to attack or defend. In their reports on the situation in the area of the Kursk Bulge, Zhukov and Vasilevsky proposed to bleed the enemy in a defensive battle, and then go on the counteroffensive. A number of military leaders opposed - Vatutin, Malinovsky, Timoshenko, Voroshilov - but Stalin supported the decision to defend, fearing that as a result of our offensive, the Nazis would be able to break through the front line. The final decision was made in late May - early June, when.
“The real course of events showed that the decision to deliberately defend was the most rational type of strategic action,” emphasizes military historian, Candidate of Historical Sciences Yuri Popov.2. In terms of the number of troops, the battle exceeded the scale of the Battle of Stalingrad The Battle of Kursk is still considered one of the largest battles of World War II. On both sides, more than four million people were involved in it (for comparison: during the Battle of Stalingrad, a little more than 2.1 million people participated in different stages of hostilities). According to the General Staff of the Red Army, only during the offensive from July 12 to August 23, 35 German divisions were defeated, including 22 infantry, 11 tank and two motorized. The remaining 42 divisions suffered heavy losses and largely lost their combat effectiveness. In the Battle of Kursk, the German command used 20 tank and motorized divisions out of a total of 26 divisions that were available at that time on the Soviet-German front. After Kursk, 13 of them were completely defeated. 3. Information about the plans of the enemy was promptly received from scouts from abroad Soviet military intelligence was able to timely reveal the preparation of the German army for a major offensive on the Kursk salient. Foreign residencies obtained information in advance about Germany's preparations for the spring-summer campaign of 1943. So, on March 22, the GRU resident in Switzerland, Sandor Rado, reported that for “... an attack on Kursk, the SS tank corps would probably be used (the organization is banned in the Russian Federation - approx. ed.), which is currently receiving replenishment.” And intelligence officers in England (GRU resident, Major General I. A. Sklyarov) obtained an analytical report prepared for Churchill "Assessment of possible German intentions and actions in the Russian campaign of 1943."
"The Germans will concentrate their forces to eliminate the Kursk salient," the document said.Thus, the information obtained by the scouts in early April revealed in advance the plan of the enemy's summer campaign and made it possible to preempt the enemy's strike. 4. The Kursk Bulge became a large-scale baptism of fire for Smersh The Smersh counterintelligence agencies were formed in April 1943 - three months before the start of the historic battle. "Death to Spies!" - so succinctly and at the same time succinctly defined the main task of this special service, Stalin. But the Smershevites not only reliably protected units and formations of the Red Army from enemy agents and saboteurs, but also, which was used by the Soviet command, conducted radio games with the enemy, carried out combinations to bring German agents to our side. The book "The Fiery Arc": The Battle of Kursk through the Eyes of the Lubyanka, published on the basis of the materials of the Central Archive of the FSB of Russia, tells about a whole series of Chekist operations in that period.
 So, in order to misinform the German command, the Smersh Directorate of the Central Front and the Smersh Department of the Oryol Military District conducted a successful radio game "Experience". It lasted from May 1943 to August 1944. The work of the radio station was legendary on behalf of the reconnaissance group of Abwehr agents and misled the German command about the plans of the Red Army, including in the Kursk region. In total, 92 radiograms were transmitted to the enemy, 51 were received. Several German agents were called to our side and neutralized, cargo dropped from the aircraft was received (weapons, money, fictitious documents, uniforms). . 5. On the Prokhorovsky field, the number of tanks fought against their quality This settlement began what is believed to be the largest battle of armored vehicles for the entire time of the Second World War. On both sides, up to 1,200 tanks and self-propelled guns took part in it. The Wehrmacht had superiority over the Red Army due to the greater efficiency of its equipment. For example, the T-34 had only a 76-mm cannon, and the T-70 had a 45-mm gun. The Churchill III tanks, received by the USSR from England, had a 57 mm gun, but this vehicle was notable for its low speed and poor maneuverability. In turn, the German heavy tank T-VIH "Tiger" had an 88-mm cannon, with a shot from which it pierced the armor of the thirty-four at a distance of up to two kilometers.
So, in order to misinform the German command, the Smersh Directorate of the Central Front and the Smersh Department of the Oryol Military District conducted a successful radio game "Experience". It lasted from May 1943 to August 1944. The work of the radio station was legendary on behalf of the reconnaissance group of Abwehr agents and misled the German command about the plans of the Red Army, including in the Kursk region. In total, 92 radiograms were transmitted to the enemy, 51 were received. Several German agents were called to our side and neutralized, cargo dropped from the aircraft was received (weapons, money, fictitious documents, uniforms). . 5. On the Prokhorovsky field, the number of tanks fought against their quality This settlement began what is believed to be the largest battle of armored vehicles for the entire time of the Second World War. On both sides, up to 1,200 tanks and self-propelled guns took part in it. The Wehrmacht had superiority over the Red Army due to the greater efficiency of its equipment. For example, the T-34 had only a 76-mm cannon, and the T-70 had a 45-mm gun. The Churchill III tanks, received by the USSR from England, had a 57 mm gun, but this vehicle was notable for its low speed and poor maneuverability. In turn, the German heavy tank T-VIH "Tiger" had an 88-mm cannon, with a shot from which it pierced the armor of the thirty-four at a distance of up to two kilometers.  Our tank, on the other hand, could penetrate 61 mm thick armor at a distance of a kilometer. By the way, the frontal armor of the same T-IVH reached a thickness of 80 millimeters. It was possible to fight with the hope of success in such conditions only in close combat, which was applied, however, at the cost of heavy losses. Nevertheless, near Prokhorovka, the Wehrmacht lost 75% of its tank resources. For Germany, such losses were catastrophic and proved difficult to replace almost until the very end of the war. 6. Cognac of General Katukov did not reach the Reichstag During the Battle of Kursk, for the first time in the years of the war, the Soviet command used large tank formations in echelon to hold a defensive zone on a broad front. One of the armies was commanded by Lieutenant General Mikhail Katukov, future twice Hero of the Soviet Union, marshal of the armored forces. Subsequently, in his book "On the Edge of the Main Strike", in addition to the difficult moments of his front-line epic, he recalled one funny incident related to the events of the Battle of Kursk.
Our tank, on the other hand, could penetrate 61 mm thick armor at a distance of a kilometer. By the way, the frontal armor of the same T-IVH reached a thickness of 80 millimeters. It was possible to fight with the hope of success in such conditions only in close combat, which was applied, however, at the cost of heavy losses. Nevertheless, near Prokhorovka, the Wehrmacht lost 75% of its tank resources. For Germany, such losses were catastrophic and proved difficult to replace almost until the very end of the war. 6. Cognac of General Katukov did not reach the Reichstag During the Battle of Kursk, for the first time in the years of the war, the Soviet command used large tank formations in echelon to hold a defensive zone on a broad front. One of the armies was commanded by Lieutenant General Mikhail Katukov, future twice Hero of the Soviet Union, marshal of the armored forces. Subsequently, in his book "On the Edge of the Main Strike", in addition to the difficult moments of his front-line epic, he recalled one funny incident related to the events of the Battle of Kursk. “In June 1941, after leaving the hospital, on the way to the front, I popped into a store and bought a bottle of cognac, deciding that I would drink it with my comrades as soon as I won the first victory over the Nazis,” the front-line soldier wrote. - Since then, this cherished bottle has traveled with me on all fronts. And finally, the long-awaited day has come. We arrived at the CP. The waitress quickly fried the eggs, I took a bottle out of my suitcase. They sat down with their comrades at a simple wooden table. Cognac was poured, which brought back pleasant memories of a peaceful pre-war life. And the main toast - "To victory! To Berlin!"7. In the sky over Kursk, the enemy was smashed by Kozhedub and Maresyev During the Battle of Kursk, many Soviet soldiers showed heroism.
“Every day of fighting gave many examples of courage, bravery, stamina of our soldiers, sergeants and officers,” notes retired Colonel-General Alexei Kirillovich Mironov, participant in the Great Patriotic War. “They deliberately sacrificed themselves, trying to prevent the enemy from passing through their defense sector.”
Over 100 thousand participants in those battles were awarded orders and medals, 231 became Heroes of the Soviet Union. 132 formations and units received the title of guards, and 26 were awarded the honorary titles of Oryol, Belgorod, Kharkov and Karachev. Future three times Hero of the Soviet Union. Alexei Maresyev also took part in the battles. On July 20, 1943, during an air battle with superior enemy forces, he saved the lives of two Soviet pilots by destroying two enemy FW-190 fighters at once. On August 24, 1943, the deputy squadron commander of the 63rd Guards Fighter Aviation Regiment, Senior Lieutenant A.P. Maresyev, was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union. 8. The defeat in the Battle of Kursk was a shock to Hitler After the failure at the Kursk Bulge, the Fuhrer was furious: he lost the best connections, not yet knowing that in the fall he would have to leave the entire Left-Bank Ukraine. Without changing his character, Hitler immediately laid the blame for the Kursk failure on the field marshals and generals who were in direct command of the troops. Field Marshal Erich von Manstein, who developed and conducted Operation Citadel, later wrote:
“This was the last attempt to keep our initiative in the East. With its failure, the initiative finally passed to the Soviet side. Therefore, Operation Citadel is a decisive turning point in the war on the Eastern Front.The German historian from the military history department of the Bundeswehr Manfred Pay wrote:
“The irony of history is that Soviet generals began to learn and develop the art of operational leadership of troops, which was highly appreciated by the German side, and the Germans themselves, under pressure from Hitler, switched to Soviet positions of tough defense - according to the principle "by all means".By the way, the fate of the elite SS tank divisions that took part in the battles on the Kursk Bulge - the Leibstandarte, the Totenkopf and the Reich - developed even more sadly in the future. All three formations participated in the battles with the Red Army in Hungary, were defeated, and the remnants made their way into the American zone of occupation. However, the SS tankers were handed over to the Soviet side, and they were punished as war criminals. 9. The victory at the Kursk Bulge brought the opening of the Second Front closer As a result of the defeat of significant Wehrmacht forces on the Soviet-German front, more favorable conditions were created for the deployment of American-British troops in Italy, the beginning of the disintegration of the fascist bloc was laid - the Mussolini regime collapsed, Italy withdrew from the war on the side of Germany. Under the influence of the victories of the Red Army, the scale of the resistance movement in the countries occupied by German troops increased, and the authority of the USSR as the leading force of the anti-Hitler coalition was strengthened. In August 1943, the US Joint Chiefs of Staff prepared an analytical document in which they assessed the role of the USSR in the war.
"Russia occupies a dominant position," the report noted, "and is a decisive factor in the forthcoming defeat of the Axis in Europe."
 It is no coincidence that President Roosevelt was aware of the danger of further delaying the opening of the Second Front. On the eve of the Tehran Conference, he told his son:
It is no coincidence that President Roosevelt was aware of the danger of further delaying the opening of the Second Front. On the eve of the Tehran Conference, he told his son: “If things in Russia continue as they are now, then perhaps next spring there will be no need for a Second Front.”Interestingly, a month after the end of the Battle of Kursk, Roosevelt already had his own plan for the dismemberment of Germany. He presented it just at a conference in Tehran. 10. For the salute in honor of the liberation of Orel and Belgorod, they used up the entire supply of blank shells in Moscow During the Battle of Kursk, two key cities of the country, Orel and Belgorod, were liberated. Joseph Stalin ordered an artillery salute to be arranged in Moscow on this occasion - the first in the entire war. It was estimated that in order for the salute to be heard throughout the city, about 100 anti-aircraft guns would have to be deployed. There were such weapons, but only 1,200 blank shells were at the disposal of the organizers of the solemn action (during the war, they were not kept in reserve in the Moscow air defense garrison). Therefore, out of 100 guns, only 12 volleys could be fired. True, the Kremlin division of mountain guns (24 guns) was also involved in the salute, blank shells for which were available. However, the effect of the action could not turn out as expected. The solution was to increase the interval between volleys: at midnight on August 5, firing from all 124 guns was carried out every 30 seconds. And in order for the salute to be heard everywhere in Moscow, groups of guns were placed in stadiums and wastelands in different parts of the capital.
In order to realize this opportunity, the German military leadership launched preparations for a major summer offensive in this direction. It hoped to defeat the main forces of the Red Army on the central sector of the Soviet-German front, by delivering a series of powerful counter-attacks, to regain the strategic initiative and change the course of the war in its favor. The concept of the operation (code name "Citadel") provided for strikes in converging directions from the north and south at the base of the Kursk ledge on the 4th day of the operation to surround and then destroy the Soviet troops. Subsequently, it was planned to strike at the rear of the Southwestern Front (Operation Panther) and launch an offensive in a northeast direction in order to reach the deep rear of the central grouping of Soviet troops and create a threat to Moscow. The best generals of the Wehrmacht and the most combat-ready troops were involved in Operation Citadel, a total of 50 divisions (including 16 tank and motorized) and a large number of individual units that were part of the 9th and 2nd armies of the army group " Center ”(Field Marshal G. Kluge), to the 4th Panzer Army and the Kempf task force of the Army Group South (Field Marshal E. Manstein). They were supported by aviation of the 4th and 6th air fleets. In total, this grouping consisted of over 900 thousand people, about 10 thousand guns and mortars, up to 2700 tanks and assault guns, and about 2050 aircraft. This amounted to about 70% of tank, up to 30% of motorized and more than 20% of infantry divisions, as well as over 65% of all combat aircraft operating on the Soviet-German front, which were concentrated on a sector that was only about 14% of its length.
In order to achieve the rapid success of its offensive, the German command relied on the massive use of armored vehicles (tanks, assault guns, armored personnel carriers) in the first operational echelon. The medium and heavy tanks T-IV, T-V ("panther"), T-VI ("tiger"), the Ferdinand assault guns, which entered service with the German army, had good armor protection and strong artillery weapons. Their 75-mm and 88-mm guns with a direct range of 1.5-2.5 km were 2.5 times the range of the 76.2-mm gun of the main Soviet T-34 tank. Due to the high initial speed of the projectiles, increased armor penetration was achieved. The Hummel and Vespe armored self-propelled howitzers, which were part of the artillery regiments of tank divisions, could also be successfully used for direct fire at tanks. In addition, excellent Zeiss optics were installed on them. This allowed the enemy to achieve a certain superiority in tank equipment. In addition, new aircraft entered service with the German aviation: the Focke-Wulf-190A fighter, the Henkel-190A and Henkel-129 attack aircraft, which were supposed to maintain air supremacy and reliable support for tank divisions.
The German command attached particular importance to the surprise operation "Citadel". To this end, it was envisaged to conduct disinformation of the Soviet troops on a large scale. To this end, intensive preparations for Operation Panther continued in the Army Zone South. Demonstrative reconnaissance was carried out, tanks were advanced, crossing facilities were concentrated, radio communications were carried out, the actions of agents were activated, rumors were spread, etc. In the band of the army group "Center", on the contrary, everything was carefully disguised. But although all the activities were carried out with great care and method, they did not give effective results.
In order to secure the rear areas of their strike groups, the German command in May-June 1943 undertook large punitive expeditions against the Bryansk and Ukrainian partisans. Thus, more than 10 divisions acted against 20 thousand Bryansk partisans, and in the Zhytomyr region the Germans attracted 40 thousand soldiers and officers. But the enemy failed to defeat the partisans.
When planning the summer-autumn campaign of 1943, the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command (VGK) planned to conduct a broad offensive, delivering the main blow in the south-western direction in order to defeat Army Group South, liberate the Left-Bank Ukraine, Donbass and overcome the river. Dnieper.
The Soviet command began to develop a plan for the upcoming actions for the summer of 1943 immediately after the end of the winter campaign at the end of March 1943. The Supreme Command Headquarters, the General Staff, all front commanders who defended the Kursk ledge took part in the development of the operation. The plan provided for the main attack in the south-western direction. Soviet military intelligence was able to timely reveal the preparation of the German army for a major offensive on the Kursk Bulge and even set a date for the start of the operation.
The Soviet command faced a difficult task - to choose a course of action: attack or defend. In his report on April 8, 1943 to the Supreme Commander-in-Chief with an assessment of the general situation and his thoughts on the actions of the Red Army for the summer of 1943 in the Kursk Bulge region, the marshal reported: . It would be better if we exhaust the enemy on our defenses, knock out his tanks, and then, introducing fresh reserves, by going over to the general offensive, we finally finish off the main enemy grouping. The chief of the general staff adhered to the same views: “A thorough analysis of the situation and foresight of the development of events made it possible to draw the correct conclusion: the main efforts must be concentrated north and south of Kursk, bleed the enemy here in a defensive battle, and then go on the counteroffensive and defeat him” .
As a result, an unprecedented decision was made to go over to the defensive in the area of the Kursk salient. The main efforts were concentrated in the areas north and south of Kursk. There was a case in the history of the war when the strongest side, which had everything necessary for the offensive, chose from several possible options the most optimal course of action - defense. Not everyone agreed with this decision. The commanders of the Voronezh and Southern fronts, the generals, continued to insist on a preemptive strike in the Donbass. They were supported, and some others. The final decision was made in late May - early June, when it became known exactly about the "Citadel" plan. Subsequent analysis and the actual course of events showed that the decision to deliberately defend in the face of significant superiority in forces in this case was the most rational type of strategic action.
The final decision for the summer and autumn of 1943 was drawn up by the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command in mid-April: the German occupiers were to be driven out of the Smolensk-r. Sozh - the middle and lower reaches of the Dnieper, crush the so-called defensive "eastern rampart" of the enemy, and also eliminate the enemy foothold in the Kuban. The main blow in the summer of 1943 was supposed to be delivered in the southwestern direction, and the second in the western direction. On the Kursk ledge, it was decided to deplete and bleed the shock groups of German troops by deliberate defense, and then complete their defeat by going over to the counteroffensive. The main efforts were concentrated in the areas north and south of Kursk. The events of the first two years of the war showed that the defense of the Soviet troops did not always withstand the massive attacks of the enemy, which led to tragic consequences.
To this end, it was supposed to make the most of the advantages of a pre-created multi-lane defense, bleed the enemy's main tank groupings, wear out his most combat-ready troops, and gain strategic air supremacy. Then, going over to a decisive counteroffensive, complete the defeat of the enemy groupings in the area of the Kursk ledge.
The troops of the Central and Voronezh fronts were mainly involved in the defensive operation near Kursk. The headquarters of the Supreme High Command understood that the transition to deliberate defense was associated with a certain risk. Therefore, by April 30, the Reserve Front was formed (later renamed the Steppe Military District, and from July 9 - the Steppe Front). It included the 2nd reserve, 24th, 53rd, 66th, 47th, 46th, 5th guards tank armies, 1st, 3rd and 4th guards, 3rd, 10th and 18th tank armies, 1st and 5th th mechanized corps. All of them were stationed in the areas of Kastornoye, Voronezh, Bobrovo, Millerovo, Rossosh and Ostrogozhsk. The field control of the front was located not far from Voronezh. Five tank armies, a number of separate tank and mechanized corps, a large number of rifle corps and divisions were concentrated in the reserve of the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command (RVGK), as well as in the second echelons of the fronts, at the direction of the Supreme High Command. From April 10 to July, the Central and Voronezh Fronts received 10 rifle divisions, 10 anti-tank artillery brigades, 13 separate anti-tank artillery regiments, 14 artillery regiments, eight guards mortar regiments, seven separate tank and self-propelled artillery regiments. In total, 5635 guns, 3522 mortars, 1284 aircraft were transferred to two fronts.
By the beginning of the Battle of Kursk, the Central and Voronezh Fronts and the Steppe Military District included 1909 thousand people, more than 26.5 thousand guns and mortars, over 4.9 thousand tanks and self-propelled artillery installations (ACS), about 2.9 thousand aircraft.
After achieving the goals of the strategic defensive operation, it was planned that the Soviet troops would go over to the counteroffensive. At the same time, the defeat of the Oryol grouping of the enemy (plan "Kutuzov") was assigned to the troops of the left wing of the Western (Colonel-General V.D. Sokolovsky), Bryansk (Colonel-General) and the right wing of the Central Fronts. The offensive operation in the Belgorod-Kharkov direction (the plan "Commander Rumyantsev") was planned to be carried out by the forces of the Voronezh and Steppe fronts in cooperation with the troops of the Southwestern Front (General of the Army R.Ya. Malinovsky). The coordination of the actions of the troops of the fronts was entrusted to the representatives of the Headquarters of the Supreme Command of Marshals of the Soviet Union G.K. Zhukov and A.M. Vasilevsky, colonel-general of artillery, and aviation - to air marshal.
The troops of the Central, Voronezh Fronts and the Steppe Military District created a powerful defense, which included 8 defensive lines and lines with a total depth of 250-300 km. The defense was built as an anti-tank, anti-artillery and anti-aircraft defense with a deep separation of battle formations and fortifications, with a widely developed system of strong points, trenches, communications and barriers.
On the left bank of the Don, a state line of defense was equipped. The depth of the defense lines was 190 km on the Central Front, and 130 km on the Voronezh Front. At each front, three army and three front defensive lines were created, equipped in engineering terms.
Both fronts had six armies each: the Central Front - 48, 13, 70, 65, 60th combined arms and 2nd tank; Voronezh - 6th, 7th guards, 38th, 40th, 69th combined arms and 1st tank. The width of the defense lines of the Central Front was 306 km, and the Voronezh - 244 km. All combined-arms armies were located in the first echelon on the Central Front, and four combined-arms armies were located on the Voronezh Front.
The commander of the Central Front, General of the Army, having assessed the situation, came to the conclusion that the enemy would deliver the main blow in the direction of Olkhovatka in the defense zone of the 13th Combined Arms Army. Therefore, it was decided to reduce the width of the defense zone of the 13th Army from 56 to 32 km and bring its composition to four rifle corps. Thus, the composition of the armies increased to 12 rifle divisions, and its operational formation became two-echelon.
Commander of the Voronezh Front, General N.F. It was more difficult for Vatutin to determine the direction of the enemy's main attack. Therefore, the defense zone of the 6th Guards Combined Arms Army (it was she who defended herself in the direction of the main attack of the 4th tank army of the enemy) was 64 km. In the presence of two rifle corps and one rifle division in its composition, the army commander was forced to build army troops in one echelon, allocating only one rifle division to the reserve.
Thus, the depth of defense of the 6th Guards Army initially turned out to be less than the depth of the strip of the 13th Army. Such an operational formation led to the fact that the commanders of rifle corps, trying to create a defense as deep as possible, built a battle formation in two echelons.
Great importance was attached to the creation of artillery groupings. Particular attention was paid to the massing of artillery in the likely directions of enemy strikes. On April 10, 1943, the People's Commissar of Defense issued a special order on the use of the artillery of the reserve of the High Command in battle, the assignment of reinforcement artillery regiments to the armies and the formation of anti-tank and mortar brigades for the fronts.
In the defense zones of the 48th, 13th and 70th armies of the Central Front, on the intended direction of the main attack of Army Group Center, 70% of all guns and mortars of the front and 85% of all artillery of the RVGK were concentrated (including the second echelon and reserves of the front). Moreover, 44% of the artillery regiments of the RVGK were concentrated in the zone of the 13th Army, where the point of impact of the main enemy forces was aimed. This army, which had 752 guns and mortars with a caliber of 76 mm and above, was given the 4th breakthrough artillery corps, which had 700 guns and mortars and 432 rocket artillery installations, for reinforcement. This saturation of the army with artillery made it possible to create a density of up to 91.6 guns and mortars per 1 km of the front (including 23.7 anti-tank guns). There was no such density of artillery in any of the previous defensive operations.
Thus, the desire of the command of the Central Front to solve the problems of the insurmountability of the defense being created already in the tactical zone, not giving the enemy the opportunity to break out of it, clearly loomed, which significantly complicated the further struggle.
The problem of using artillery in the defense zone of the Voronezh Front was solved somewhat differently. Since the troops of the front were built in two echelons, the artillery was distributed between the echelons. But even on this front, in the main direction, which accounted for 47% of the entire front defense zone, where the 6th and 7th Guards Armies were stationed, it was possible to create a sufficiently high density - 50.7 guns and mortars per 1 km of the front. 67% of the guns and mortars of the front and up to 66% of the RVGK artillery (87 out of 130 artillery regiments) were concentrated in this direction.
The command of the Central and Voronezh fronts paid great attention to the use of anti-tank artillery. They included 10 anti-tank brigades and 40 separate regiments, of which seven brigades and 30 regiments, that is, the vast majority of anti-tank weapons, were located on the Voronezh Front. On the Central Front, more than one third of all artillery anti-tank weapons became part of the artillery anti-tank reserve of the front, as a result, the commander of the Central Front, K.K. Rokossovsky got the opportunity to quickly use his reserves to fight enemy tank groups in the most threatened areas. On the Voronezh front, the bulk of the anti-tank artillery was transferred to the armies of the first echelon.
Soviet troops outnumbered the enemy grouping opposing them near Kursk in personnel by 2.1, artillery - by 2.5, tanks and self-propelled guns - by 1.8, aircraft - by 1.4 times.
On the morning of July 5, the main forces of the enemy strike groupings, weakened by the pre-emptive artillery counter-preparation of the Soviet troops, went on the offensive, throwing up to 500 tanks and assault guns against the defenders in the Orel-Kursk direction, and about 700 tanks and assault guns in the Belgorod-Kursk direction. German troops attacked the entire defense zone of the 13th Army and the flanks of the 48th and 70th armies adjoining it in a 45 km wide zone. The main blow was delivered by the northern enemy grouping with the forces of three infantry and four tank divisions to Olkhovatka against the troops of the left flank of the 13th army of the general. Four infantry divisions advanced against the right flank of the 13th and the left flank of the 48th Army (commander - general) to Maloarkhangelsk. Three infantry divisions attacked the right flank of the General's 70th Army in the direction of Gnilets. The advance of the ground forces was supported by air strikes. Heavy and stubborn battles ensued. The command of the 9th German Army, which did not expect to meet such a powerful rebuff, was forced to repeat an hour-long artillery preparation. In increasingly fierce battles, warriors of all branches of the armed forces fought heroically.

Defensive operations of the Central and Voronezh fronts during the Battle of Kursk
But the enemy tanks, despite the losses, continued to stubbornly move forward. The front command promptly reinforced the troops defending in the Olkhovat direction with tanks, self-propelled artillery mounts, rifle formations, field and anti-tank artillery. The enemy, intensifying the actions of his aviation, also brought heavy tanks into battle. On the first day of the offensive, he managed to break through the first line of defense of the Soviet troops, advance 6-8 km and reach the second line of defense in the area north of Olkhovatka. In the direction of Gnilets and Maloarkhangelsk, the enemy was able to advance only 5 km.
Having met the stubborn resistance of the defending Soviet troops, the German command brought into battle almost all the formations of the attack group of the Army Group Center, but they could not break through the defense. In seven days, they managed to advance only 10-12 km, without breaking through the tactical defense zone. By July 12, the enemy's offensive capabilities on the northern face of the Kursk Bulge had dried up, he stopped his attacks and went on the defensive. It should be noted that the enemy did not conduct active offensive operations in other directions in the defense zone of the troops of the Central Front.
Having repelled enemy attacks, the troops of the Central Front began to prepare for offensive operations.
On the southern face of the Kursk salient, in the zone of the Voronezh Front, the struggle was also of an exceptionally tense character. As early as July 4, the forward detachments of the 4th German Tank Army tried to shoot down the outposts of the General's 6th Guards Army. By the end of the day, they managed to reach the front line of the army's defense at several points. On July 5, the main forces began to operate in two directions - on Oboyan and Korocha. The main blow fell on the 6th Guards Army, and the auxiliary - on the 7th Guards Army from the Belgorod region to Korocha.
.jpg)
Memorial "Beginning of the Battle of Kursk on the southern ledge". Belgorod region
The German command sought to build on the success achieved by continuing to build up its efforts along the Belgorod-Oboyan highway. By the end of July 9, the 2nd SS Panzer Corps not only broke through to the army (third) defense line of the 6th Guards Army, but also managed to wedge into it about 9 km southwest of Prokhorovka. However, he failed to break into the operational space.
On July 10, Hitler ordered the commander of Army Group South to bring about a decisive turning point in the course of the battle. Convinced of the complete impossibility of breaking the resistance of the troops of the Voronezh Front in the Oboyan direction, Field Marshal E. Manstein decided to change the direction of the main attack and now advance on Kursk in a roundabout way - through Prokhorovka. At the same time, an auxiliary strike group attacked Prokhorovka from the south. The 2nd SS Panzer Corps was brought up to the Prokhorovka direction, which included the elite divisions "Reich", "Dead Head", "Adolf Hitler", as well as parts of the 3rd Panzer Corps.
Having discovered the maneuver of the enemy, the front commander, General N.F. Vatutin advanced the 69th Army in this direction, and then the 35th Guards Rifle Corps. In addition, the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command decided to strengthen the Voronezh Front at the expense of strategic reserves. As early as July 9, she ordered the general commander of the Steppe Front to move the 4th Guards, 27th and 53rd armies to the Kursk-Belgorod direction and transfer them to General N.F. Vatutin 5th Guards and 5th Guards Tank Armies. The troops of the Voronezh Front were to thwart the enemy's offensive by inflicting a powerful counterattack (five armies) on his grouping, wedged in the Oboyan direction. However, on July 11, it was not possible to launch a counterattack. On this day, the enemy captured the line planned for the deployment of tank formations. Only by bringing into battle four rifle divisions and two tank brigades of the 5th Guards Tank Army, the general managed to stop the enemy two kilometers from Prokhorovka. Thus, the oncoming battles of the forward detachments and units in the Prokhorovka area began already on July 11.
.jpg)
Tankers, in cooperation with the infantry, counterattack the enemy. Voronezh front. 1943
On July 12, both opposing groups went on the offensive, striking in the Prokhorovka direction on both sides of the Belgorod-Kursk railway. A fierce battle unfolded. The main events took place southwest of Prokhorovka. From the northwest, formations of the 6th Guards and 1st Tank armies attacked Yakovlevo. And from the northeast, from the Prokhorovka area, in the same direction, the 5th Guards Tank Army with attached two tank corps and the 33rd Guards Rifle Corps of the 5th Guards Combined Arms Army attacked in the same direction. To the east of Belgorod, the strike was undertaken by rifle formations of the 7th Guards Army. After a 15-minute artillery raid, the 18th and 29th tank corps of the 5th Guards Tank Army and the 2nd and 2nd Guards Tank Corps attached to it on the morning of July 12 went on the offensive in the general direction of Yakovlevo.
Even earlier, at dawn, on the river. Psyol in the defense zone of the 5th Guards Army, the tank division "Dead Head" launched an offensive. However, the divisions of the SS Panzer Corps "Adolf Hitler" and "Reich", which directly opposed the 5th Guards Tank Army, remained on the occupied lines, having prepared them overnight for defense. On a rather narrow section from Berezovka (30 km northwest of Belgorod) to Olkhovatka, a battle took place between two tank strike groups. The battle went on all day. Both sides suffered heavy losses. The fight was extremely fierce. The losses of the Soviet tank corps amounted to 73% and 46%, respectively.
As a result of a fierce battle in the Prokhorovka region, none of the parties was able to solve the tasks assigned to it: the Germans - to break through to the Kursk region, and the 5th Guards Tank Army - to reach the Yakovlevo region, defeating the opposing enemy. But the enemy's path to Kursk was closed. The motorized divisions of the SS "Adolf Hitler", "Reich" and "Dead Head" stopped the attacks and entrenched themselves on the achieved lines. The 3rd German tank corps advancing on Prokhorovka from the south was able to push the formations of the 69th army by 10-15 km that day. Both sides suffered heavy losses.
.jpg)
The collapse of hope.
German soldier on the Prokhorovsky field
Despite the fact that the counterattack of the Voronezh Front slowed down the advance of the enemy, it did not achieve the goals set by the Supreme Command Headquarters.
In fierce battles on July 12 and 13, the enemy strike force was stopped. However, the German command did not abandon its intention to break through to Kursk, bypassing Oboyan from the east. In turn, the troops participating in the counterattack of the Voronezh Front did everything to fulfill the tasks assigned to them. The confrontation between the two groups - the advancing German and the Soviet counterattack - continued until July 16, mainly on the lines that they occupied. In these 5-6 days (after July 12) there were continuous battles with enemy tanks and infantry. Attacks and counterattacks followed each other day and night.
.jpg)
On the Belgorod-Kharkov direction. Broken enemy equipment after a Soviet air raid
On July 16, the 5th Guards Army and its neighbors received an order from the commander of the Voronezh Front to switch to a tough defense. The next day, the German command began to withdraw its troops to their original positions.
One of the reasons for the failure was that the most powerful grouping of Soviet troops struck at the most powerful enemy grouping, but not in the flank, but in the forehead. The Soviet command did not use the favorable configuration of the front, which made it possible to strike under the base of the enemy penetration in order to encircle and subsequently destroy the entire grouping of German troops operating north of Yakovlevo. In addition, Soviet commanders and staffs, the troops as a whole, did not yet properly master combat skills, and military leaders did not yet possess the art of the offensive. There were also omissions in the interaction of infantry with tanks, ground forces with aviation, between formations and units.
On the Prokhorovsky field, the number of tanks fought against their quality. The 5th Guards Tank Army had 501 T-34 tanks with a 76-mm cannon, 264 T-70 light tanks with a 45-mm cannon, and 35 Churchill III heavy tanks with a 57-mm cannon received by the USSR from England. This tank had very low speed and poor maneuverability. Each corps had a regiment of SU-76 self-propelled artillery mounts, but not a single SU-152. The Soviet medium tank had the ability to pierce armor 61 mm thick at a distance of 1000 m and 69 mm thick at 500 m with an armor-piercing projectile. Tank armor: frontal - 45 mm, side - 45 mm, turret - 52 mm. The German medium tank T-IVH had armor thickness: frontal - 80 mm, side - 30 mm, turret - 50 mm. The armor-piercing projectile of its 75-mm cannon at a range of up to 1500 m pierced armor over 63 mm. The German heavy tank T-VIH "Tiger" with an 88-mm gun had armor: frontal - 100 mm, side - 80 mm, towers - 100 mm. Its armor-piercing projectile pierced armor 115 mm thick. He pierced the armor of the thirty-four at a distance of up to 2000 m.
.jpg)
A company of American M3s General Lee tanks supplied to the USSR under Lend-Lease is advancing to the front line of defense of the Soviet 6th Guards Army. July 1943
The 2nd SS Panzer Corps, which opposed the army, had 400 modern tanks: about 50 heavy tanks "tiger" (88-mm cannon), dozens of high-speed (34 km / h) medium tanks "panther", modernized T-III and T-IV ( cannon 75 mm) and heavy assault guns "Ferdinand" (cannon 88 mm). To hit a heavy tank, the T-34 had to approach it by 500 m, which was far from always possible; the rest of the Soviet tanks had to come even closer. In addition, the Germans placed some of their tanks in caponiers, which ensured their invulnerability from the side. Fighting with the hope of success in such conditions was possible only in close combat. As a result, losses increased. Near Prokhorovka, Soviet troops lost 60% of tanks (500 out of 800), while German troops lost 75% (300 out of 400; according to German data, 80-100). For them it was a disaster. For the Wehrmacht, such losses were difficult to replace.
The repulse of the most powerful blow by the troops of the Army Group "South" was achieved as a result of the joint efforts of the formations and troops of the Voronezh Front with the participation of strategic reserves. Thanks to the courage, steadfastness and heroism of soldiers and officers of all branches of the armed forces.
.jpg)
Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul on the Prokhorovsky field
The counteroffensive of the Soviet troops began on July 12 with strikes from the northeast and east of the formations of the left wing of the Western and troops of the Bryansk Fronts against the German 2nd Tank Army and the 9th Army of Army Group Center, which were defending in the Oryol direction. On July 15, troops of the Central Front attacked Kromy from the south and southeast.

Soviet counteroffensive during the Battle of Kursk
Concentric strikes by troops from the fronts broke through the enemy's defenses in depth. Advancing in converging directions on Oryol, Soviet troops liberated the city on August 5. Pursuing the retreating enemy, by August 17-18 they reached the Hagen defensive line, prepared in advance by the enemy on the outskirts of Bryansk.
.jpg)
As a result of the Oryol operation, Soviet troops defeated the enemy's Oryol grouping (defeated 15 divisions) and advanced westward up to 150 km.
.jpg)
Residents of the liberated city of Orel and Soviet soldiers at the entrance to the cinema before showing the newsreel-documentary film "Battle of Oryol". 1943
The troops of the Voronezh (from July 16) and the Steppe (from July 19) fronts, pursuing the retreating enemy troops, by July 23 reached the lines occupied before the start of the defensive operation, and on August 3 launched a counteroffensive in the Belgorod-Kharkov direction.
.jpg)
Forcing the Seversky Donets by soldiers of the 7th Guards Army. Belgorod. July 1943
With a swift blow, their armies defeated the troops of the German 4th Panzer Army and the Kempf task force, and liberated Belgorod on August 5.
.jpg)
Soldiers of the 89th Belgorod-Kharkov Guards Rifle Division
pass along the street of Belgorod. August 5, 1943
.jpg)
The Battle of Kursk was one of the largest battles of World War II. On both sides, more than 4 million people, over 69 thousand guns and mortars, more than 13 thousand tanks and self-propelled guns, up to 12 thousand aircraft were involved in it. Soviet troops defeated 30 divisions (including 7 tank) of the enemy, whose losses amounted to over 500 thousand people, 3 thousand guns and mortars, more than 1.5 thousand tanks and assault guns, over 3.7 thousand aircraft . The failure of Operation Citadel forever buried the myth created by Nazi propaganda about the “seasonality” of Soviet strategy, that the Red Army could only advance in winter. The collapse of the offensive strategy of the Wehrmacht once again showed the adventurism of the German leadership, which overestimated the capabilities of its troops and underestimated the strength of the Red Army. The Battle of Kursk led to a further change in the balance of forces on the front in favor of the Soviet Armed Forces, finally secured their strategic initiative and created favorable conditions for the deployment of a general offensive on a broad front. The defeat of the enemy at the "Fiery Arc" was an important step in achieving a radical turning point in the course of the war, the overall victory of the Soviet Union. Germany and its allies were forced to go on the defensive in all theaters of World War II.
.jpg)
Cemetery of German soldiers near Glazunovka station. Oryol region
As a result of the defeat of significant Wehrmacht forces on the Soviet-German front, more favorable conditions were created for the deployment of American-British troops in Italy, the beginning of the disintegration of the fascist bloc was laid - the Mussolini regime collapsed, and Italy withdrew from the war on the side of Germany. Under the influence of the victories of the Red Army, the scale of the resistance movement in the countries occupied by German troops increased, and the authority of the USSR as the leading force of the anti-Hitler coalition was strengthened.
In the Battle of Kursk, the level of military art of the Soviet troops increased. In the field of strategy, the Soviet Supreme High Command creatively approached the planning of the summer-autumn campaign of 1943. The peculiarity of the decision was expressed in the fact that the side that had the strategic initiative and overall superiority in forces went over to the defensive, deliberately giving an active role to the enemy in the initial phase of the campaign. Subsequently, as part of a single process of campaigning, following the defense, it was planned to switch to a decisive counteroffensive and deploy a general offensive in order to liberate the Left-Bank Ukraine, Donbass and overcome the Dnieper. The problem of creating an insurmountable defense on an operational-strategic scale was successfully solved. Its activity was ensured by the saturation of the fronts with a large number of mobile troops (3 tank armies, 7 separate tank and 3 separate mechanized corps), artillery corps and artillery divisions of the RVGK, formations and units of anti-tank and anti-aircraft artillery. It was achieved by carrying out artillery counter-preparation on the scale of two fronts, extensive maneuvering of strategic reserves to reinforce them, and delivering massive air strikes against enemy groupings and reserves. The headquarters of the Supreme High Command skillfully determined the plan of conducting a counteroffensive in each direction, creatively approaching the choice of the directions of the main attacks and methods of defeating the enemy. Thus, in the Oryol operation, Soviet troops used concentric strikes in converging directions, followed by fragmentation and destruction of the enemy grouping in parts. In the Belgorod-Kharkov operation, the main blow was delivered by the adjacent flanks of the fronts, which ensured a quick break-in of the enemy's strong and deep defenses, cutting his grouping into two parts and the exit of Soviet troops to the rear of the enemy's Kharkov defensive area.
In the Battle of Kursk, the problem of creating large strategic reserves and their effective use was successfully solved, and strategic air supremacy was finally won, which was held by Soviet aviation until the end of the Great Patriotic War. The headquarters of the Supreme High Command skillfully carried out strategic interaction not only between the fronts participating in the battle, but also with those operating in other directions (the troops of the Southwestern and Southern fronts on the pp. Seversky Donets and Mius fettered the actions of German troops on a wide front, which made it difficult for the Wehrmacht command to transfer from here his troops near Kursk).
The operational art of the Soviet troops in the Battle of Kursk for the first time solved the problem of creating a deliberate positional insurmountable and active operational defense up to 70 km deep. The deep operational formation of the troops of the fronts made it possible during a defensive battle to firmly hold the second and army defense lines and front lines, preventing the enemy from breaking through into the operational depth. High activity and greater stability of the defense were given by a wide maneuver of the second echelons and reserves, artillery counter-preparation and counter-attacks. During the counteroffensive, the problem of breaking through the enemy’s defense in depth was successfully solved by decisive massing of forces and means in the breakthrough areas (from 50 to 90% of their total number), skillful use of tank armies and corps as mobile groups of fronts and armies, close interaction with aviation , which carried out in full on the scale of the fronts an air offensive, which to a large extent ensured the high pace of the offensive of the ground forces. Valuable experience was gained in conducting tank battles both in a defensive operation (near Prokhorovka) and during an offensive when repelling counterattacks by large enemy armored groupings (in the areas of Bogodukhov and Akhtyrka). The problem of ensuring stable command and control of troops in operations was solved by bringing command posts closer to the combat formations of the troops and the widespread introduction of radio equipment in all organs and command posts.
.jpg)
Memorial complex "Kursk Bulge". Kursk
At the same time, during the Battle of Kursk, there were also significant shortcomings that negatively affected the course of hostilities and increased the losses of the Soviet troops, which amounted to: irretrievable - 254,470 people, sanitary - 608,833 people. They were partly due to the fact that by the beginning of the enemy offensive, the development of a plan for artillery counter-preparation in the fronts had not been completed, because. reconnaissance could not accurately identify the places of concentration of troops and placement of targets on the night of July 5. The counter-preparation began prematurely, when the enemy troops had not yet fully taken up their starting position for the offensive. In a number of cases, fire was fired at the squares, which allowed the enemy to avoid heavy losses, put the troops in order in 2.5-3 hours, go on the offensive and on the first day wedged into the defense of the Soviet troops for 3-6 km. The counterattacks of the fronts were hastily prepared and often delivered against the enemy, who had not exhausted his offensive potential, so they did not reach the final goal and ended with the transition of the counterattacking troops to the defense. During the Oryol operation, excessive haste was allowed during the transition to the offensive, not due to the situation.
In the Battle of Kursk, Soviet soldiers showed courage, steadfastness and mass heroism. Over 100 thousand people were awarded orders and medals, 231 people were awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union, 132 formations and units received the title of guards, 26 were awarded the honorary titles of Oryol, Belgorod, Kharkov and Karachev.
The material was prepared by the Research Institute
(military history) Military Academy
General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
(Illustrations are used from the book The Arc of Fire. Battle of Kursk July 5 - August 23, 1943 Moscow and / d Belfry)
The Battle of Kursk (Battle of the Kursk Bulge), which lasted from July 5 to August 23, 1943, is one of the key battles of the Great Patriotic War. In Soviet and Russian historiography, it is customary to divide the battle into three parts: the Kursk defensive operation (July 5-23); Orel (July 12 - August 18) and Belgorod-Kharkov (August 3-23) offensive.
During the winter offensive of the Red Army and the subsequent counter-offensive of the Wehrmacht in Eastern Ukraine, a ledge up to 150 km deep and up to 200 km wide was formed in the center of the Soviet-German front, facing the west (the so-called "Kursk Bulge"). The German command decided to conduct a strategic operation on the Kursk salient. For this, a military operation was developed and approved in April 1943 under the code name "Citadel". Having information about the preparation of the Nazi troops for the offensive, the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command decided to temporarily go on the defensive on the Kursk Bulge and, during the defensive battle, bleed the enemy’s strike groups and thereby create favorable conditions for the transition of Soviet troops to a counteroffensive, and then to a general strategic offensive. .
To carry out Operation Citadel, the German command concentrated 50 divisions in the area, including 18 tank and motorized divisions. The enemy grouping, according to Soviet sources, consisted of about 900 thousand people, up to 10 thousand guns and mortars, about 2.7 thousand tanks and more than 2 thousand aircraft. Air support for the German troops was provided by the forces of the 4th and 6th air fleets.
By the beginning of the Battle of Kursk, the Headquarters of the Supreme Command had created a grouping (Central and Voronezh fronts), which had more than 1.3 million people, up to 20 thousand guns and mortars, more than 3300 tanks and self-propelled guns, 2650 aircraft. The troops of the Central Front (commander - General of the Army Konstantin Rokossovsky) defended the northern front of the Kursk ledge, and the troops of the Voronezh Front (commander - General of the Army Nikolai Vatutin) - the southern front. The troops that occupied the ledge relied on the Steppe Front as part of the rifle, 3 tank, 3 motorized and 3 cavalry corps (commanded by Colonel General Ivan Konev). The fronts were coordinated by representatives of the Headquarters Marshals of the Soviet Union Georgy Zhukov and Alexander Vasilevsky.
On July 5, 1943, according to the plan of Operation Citadel, German strike groups launched an attack on Kursk from the Orel and Belgorod regions. From the side of Orel, a grouping under the command of Field Marshal Günther Hans von Kluge (Army Group Center) was advancing, from Belgorod, a grouping under the command of Field Marshal Erich von Manstein (operational group Kempf of the Army Group South).
The task of repelling the offensive from the side of Orel was entrusted to the troops of the Central Front, from the side of Belgorod - the Voronezh Front.
On July 12, in the area of the Prokhorovka railway station, 56 kilometers north of Belgorod, the largest oncoming tank battle of the Second World War took place - a battle between the advancing enemy tank group (Task Force Kempf) and the counterattacking Soviet troops. On both sides, up to 1200 tanks and self-propelled guns took part in the battle. The fierce battle lasted all day, by the evening the tank crews, together with the infantry, fought hand to hand. In one day, the enemy lost about 10 thousand people and 400 tanks and was forced to go on the defensive.
On the same day, the troops of the Bryansk, Central and left wing of the Western Fronts launched Operation Kutuzov, which had the goal of crushing the Oryol grouping of the enemy. On July 13, the troops of the Western and Bryansk fronts broke through the enemy defenses in the Bolkhov, Khotynets and Oryol directions and advanced to a depth of 8 to 25 km. On July 16, the troops of the Bryansk Front reached the line of the Oleshnya River, after which the German command began to withdraw its main forces to their original positions. By July 18, the troops of the right wing of the Central Front completely eliminated the enemy's wedge in the Kursk direction. On the same day, the troops of the Steppe Front were introduced into the battle, which began to pursue the retreating enemy.
Developing the offensive, the Soviet ground forces, supported from the air by the strikes of the forces of the 2nd and 17th air armies, as well as long-range aviation, by August 23, 1943, pushed the enemy back to the west by 140-150 km, liberated Orel, Belgorod and Kharkov. According to Soviet sources, the Wehrmacht lost 30 selected divisions in the Battle of Kursk, including 7 tank divisions, over 500 thousand soldiers and officers, 1.5 thousand tanks, more than 3.7 thousand aircraft, 3 thousand guns. The losses of the Soviet troops surpassed the German ones; they amounted to 863 thousand people. Near Kursk, the Red Army lost about 6,000 tanks.