Measures to prevent and eliminate group violations of public order, riots. Riot Prevention
The main efforts of the internal affairs bodies (law enforcement agencies) should be aimed at preventing mass riots. Forceful actions are used only when all other possibilities have been exhausted.
The most effective measures to prevent group violations of public order and riots include:
Deep analysis of emerging political, economic and social tensions, including in interethnic relations, timely informing interested authorities about them;
Collection and compilation of operational and current information about informal organizations whose activities are aimed at promoting the priority and exclusivity of one nation over another. Making proposals to interested bodies on the prohibition of their functioning. Using for the same purpose official warnings to the leaders of such organizations about the inadmissibility of violating laws, about inciting ethnic hatred;
Cooperation with the media to expose extremist movements, associations and their leaders; to explain the measures taken by the authorities and administration to relieve tension in interethnic relations; on the prevention and disclosure of criminal offenses and riots;
Identification and prosecution of persons inciting ethnic hatred, spreading false rumors that could cause group violations of public order, including riots;
Offensive, systematic work to prevent and solve crimes, bring the perpetrators to the responsibility provided for by law;
The choice of organizational and tactical schemes for the actions of the internal affairs bodies to prevent and suppress group violations of public order and riots is carried out taking into account specific circumstances. At the stage of early prevention, the internal affairs bodies solve their tasks using the usual organizational structure, using traditional, conventional forms and methods of work. At the stage of suppression, a special organizational structure (operational headquarters), a special grouping of forces and means (combined detachment) is involved, special techniques and methods of action are applied, including special operations.
The study of domestic and foreign experience in combating riots, analysis of the practice of internal affairs bodies make it possible to propose the following list of measures to improve preventive work:
Establishing direct communication with the teams of enterprises, institutions, organizations, their leaders, leaders of public organizations and informal movements;
Participation in the activities of conciliation commissions, councils of elders, etc. in the event of conflict situations;
Development of cooperation with the media;
Immediate response to statements and reports of citizens, officials, mass media about the facts of inciting ethnic or religious hatred, attempts to put pressure on public authorities and administration, about gatherings of extremist elements, criminal thieves' authorities and other circumstances that negatively affect the operational environment;
Quick and objective response to facts of violations of the law and professional ethics by employees of internal affairs bodies and other law enforcement agencies.
As noted above, group violations of public order and riots, as a rule, come from a spontaneously gathered crowd. When carrying out preventive measures, everything possible must be done to avoid rampant passions and clashes that entail the use of force. Knowledge of the various types of crowd behavior is a necessary element for the implementation of the strategy and tactics of maintaining order.
Experience shows that a crowd of people can appear in two aspects:
a) unorganized crowd- passive. The mutual arrangement of individuals in it is such that they do not react to each other. This crowd is usually submissive, easily controlled;
b) organized crowd consists of individuals who already have a different psychology. Here comes the collective consciousness, which prevails over the sense of personal responsibility. Such a mass of people can become nervous, intolerant, implacable and not afraid of threats.
The tactics of showing confidence is one of the main means of controlling the behavior of the crowd. In this case, the head of the internal affairs body responsible for ensuring public order takes the following actions in accordance with the development of the behavior of the crowd:
Conducts a dialogue with its leaders (informal leaders, organizers), in the course of which he convinces them of the inadmissibility of illegal behavior, warns of responsibility;
Asserts his authority as responsible for public order, tries to inspire respect for himself. At the same time, he must be tolerant of minor disturbances and not provoke a more serious conflict through the use of force;
The method of persuasion, as a rule, allows you to calm a large part of the crowd. But if the method of persuasion has not had its effect, the crowd continues to get excited and behaves threateningly;
Tactical methods of action of forces and means of law enforcement agencies to suppress riots can be divided into contact and non-contact.
With a non-contact method the main thing is the introduction directly into the crowd of special groupings of law enforcement forces in order to separate it, disperse and disperse it. The division of the crowd is carried out in one or more directions into several parts.
When the organizers and active participants in the riots are concentrated in the head of the crowd, it is recommended that separation and dispersal groups (in a column of at least four people) be advanced from two sides at once towards the center of the head of the crowd. When the groups approach and the active participants in the riots separate from the bulk of the crowd, one part of the column blocks the offenders, while the other forces the passive participants into the nearby streets and alleys. Removal groups and their covers are introduced into the formed corridors, which detain violators in the blocked part of the crowd and transfer them to escort groups for delivery to filtration points.
The documentation group fixes the criminal actions of the rioters, collects evidence of their guilt.
It should be borne in mind that the directions for crowding out and dispersing the crowd must be chosen in such a way that it is not driven into a dead end that would prevent its participants from leaving the place of mass disorder. It is necessary to avoid the possibility of individual actions of law enforcement officers or to allow them to become locked in a cycle of "provocation-repression".
non-contact method- this is the impact of law enforcement forces on the crowd at a distance through the use of special technical and other means provided for by law (water cannons, gas clouds, soap suds, sound amplifying installations, rubber bullets, etc.).
In the process of using such means, law enforcement forces displace the crowd in a given direction, disperse and scatter its participants. At the same time, illegal actions are recorded (using film and video recording, photography), documentation and collection of evidence of the guilt of violators and their detention.
The advantage of the non-contact method is that the end result is achieved with fewer losses among the civilian population and law enforcement forces.
The decision to use this or that method of suppressing mass riots should be made taking into account the specific conditions of the current situation and the availability of the necessary number of forces and means.
After the cessation of the riots, it is necessary to organize increased patrolling by law enforcement agencies, to carry out explanatory work among the population about the measures taken to prevent such atrocities.
Drawing a conclusion from the lecture, we can say that the protection of public order and ensuring public safety are of great importance in emergency situations. An emergency situation caused by natural, social, biological, man-made and other phenomena requires the establishment of a special legal regime, under which the internal affairs bodies have to act to maintain this regime.
It is extremely important for services, units and all employees of the internal affairs bodies to act decisively and skillfully in these difficult conditions, ensuring the personal safety of citizens and public safety, while preventing the loss of personnel, weapons, equipment and other material and technical means.
Problem 5.1. Define the term "social group".
__________________________________________________________________
Problem 5.2. What, in your opinion, is the difference between such social roles as a leader and a group leader?
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
_____
Problem 5.3. Describe the main styles of team leadership
| Authoritarian | _______________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ |
| Liberal | |
| Democratic | ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ |
Problem 5.4. Write the stages of development of spontaneous mass behavior. Explain these steps with a specific example.
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
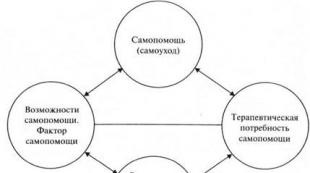
Task 5.5. Using the diagram, describe the structure of the social group.
Problem 5.6. Think of effective ways to prevent riots, stop panic and spread rumors in the following problem situations.
a) On opposite paths, two irreconcilable groups of football fans are approaching each other. They are walking along one of the central streets of Moscow. A clash of groups can lead to casualties and numerous victims, both from the conflicting "fans" and bystanders;
b) During a rock concert, the scenery caught fire due to a short circuit in the sound equipment. There was a fire on the stage and later the fire spread to the side walls of the auditorium. Panic arose in the public, which consisted mainly of minors;
c) Rumors are circulating among the members of the housing cooperative that their house in a prestigious area of the center of Moscow will be demolished, and in its place the city government plans to build a parking lot for cars in order to “unload” the main highways of the center of Moscow.
__________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
Problem 5.7. Enter the main features of an organized criminal group.
|




Problem 5.8. Small groups can be formal (formal) and informal (informal). Determine which are formal and which are informal. List the main differences between them.
Battalion of soldiers __________________
Classroom __________________
A group of children playing in the sandbox __________________
Working team __________________
A group of children cleaning the street __________________
A group of tourists traveling abroad __________________
Training platoon __________________
Teachers working in the same school __________________
Problem 5.9. Answer the question: what determines the acceptance of a certain social role and status in a group by a person.
Problem 5.10. What type of criminal group does this community of people who have committed crimes belong to?
In the city, cases of attacks on commercial firms in order to seize valuable property and money have become more frequent. The crimes were committed by a group of people, well-armed, acting in concert and debugged, quickly and cruelly. The victims reported that the perpetrators appeared suddenly and disappeared instantly.
____________________________________________________________________
Problem 5.11. Using the template provided, describe the structure of a primitive criminal group and describe the functions that members of the primitive group perform.
 |
|||||||||||
| |




| |
| |
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Problem 5.12. To describe the main phenomena characteristic of small groups, the following concepts are used: "status", "role", "imitation", "collectivism". The descriptions given illustrate the relevant intra-group phenomena. Determine what intra-group phenomena are involved.
The constant care of the team members about his
success, the desire to resist what divides them.
________________________________________________________________
Normatively given and collectively approved behavior expected from a person occupying a certain position in a group.
__________________________________________________________________
The position of a person in the system of intra-group relations, which determines his authority in the eyes of other members of the group.
_______________________________________________________________
Consciously or unconsciously following the actions and actions of other people.
_________________________________________________________________
Problem 5.13. Analyze the plot of the criminal case, determine the status of each member of the criminal group and the factors that determine this status.
Information from a criminal case. A criminal group of 6 teenagers committed a group rape of underage Katya 3. During the investigation, it was established that Katya 3. was friends with a member of this criminal group, Sasha N. A month before the crime, the group suggested Sasha to make Katya a "group girl". Sasha refused. A few days later, he lost at cards, and the group "put him on the counter." The day before the rape, the group demanded to repay the card debt or give her their girlfriend. Otherwise, he himself will be "lowered." Sasha invited Katya to the basement, where the group usually gathered. Further, the group pushed Sasha out of the basement, closed the door, leaving the common group girl Raya Zh. "on the lookout", and committed a group rape of Katya. From Katya's testimony and interrogation of the defendants, it was established that Sergei R. had raped her first, and Misha B. the last. The group then let Sasha into the basement and forced him to have sexual intercourse with the unconscious Katya.
Information about the members of the criminal group. Sergey R. - age 17, was re-educated in a special school from 11 to 14 years old, then - in a special vocational school - up to 16 years old, together with accomplice Dima V. He is friends with an adult criminal authority who "holds" this microdistrict.
Dima V. - age 16, was re-educated in a special vocational school together with Sergei R., went through the same criminal case with him. He does not study at school or at vocational schools. During the investigation of the last criminal case, he took on the role of the organizer of the robbery of the store.
Misha B. is 13 years old, goes to school, skips classes, wanders, sometimes begs. Reaches for friendship with Grisha Yu., 15 years old, the son of wealthy parents. The next two members of the criminal group: Victor K. - age 16.5, a student of vocational school, "rushes" to become the leader of the group, but he is held back by a couple of friends - Sergey and Dima. Victor goes in for sports, "shakes" his muscles. He doesn't smoke or drink, the guy is "on his mind." As for Sasha N., his age is 15 years old, and he is a newcomer to this microdistrict. His family migrated from the zone of interethnic conflict. He joined the group to avoid the oppression of other groups.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Main literature
1. Karayani A.G., Tsvetkov V.L. Psychology of communication and negotiations in extreme conditions. – M.: UNITI-DANA, 2014.
2. Karayani A.G., Tsvetkov V.L. Legal psychology: from experiment to practice. – M.: UNITI-DANA, 2013.
3. Karayani A.G., Tsvetkov V.L., Shevchenko V.M. and others. Psychology of operational-search activity - M .: UNITI-DANA, 2015.
4. Tsvetkov V.L. Legal psychology: textbook. manual for universities in schemes and comments. – M.: Shield-M, 2012.
5. Tsvetkov V.L., Khrustaleva T.A. Actual problems of management psychology in the internal affairs bodies: a study guide. - M .: Moscow University of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, 2013.
additional literature
1. Aminov I.I. Legal psychology: a textbook for universities - M. Omega-L Publishing House, 2011.
2. Eremeev S.G. Legal psychology: textbook. allowance - M .: DGSK of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, 2011.
3. Maltseva T.V., Khrustaleva T.A. Legal psychology: main issues and problems: Ref. - M.: Moscow State University of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, 2011.
4. Smirnov V.N. Legal psychology: a textbook for university students studying in the specialties "Jurisprudence" and "Psychology" - M.: UNITY-DANA, 2012.
5. Legal psychology with the basics of general and social psychology: Proc. for universities / Ed. V.Ya.Kikotya. - M.: UNITY-DANA: Law and Law, 2012.
Similar information.
Annotation The article contains an analysis of the existing problems that arise when considering issues related to the legal foundations and tasks of the actions of law enforcement organizations in conditions of riots, not only from a theoretical, but also from a practical point of view. Key words: riots, law enforcement organizations, crime prevention, crime prevention.
Among the main areas of action of law enforcement organizations, a significant place is occupied by the prevention of mass riots. Prevention is one of the main ways to prevent riots, which should directly and without fail be considered by law enforcement officials as the main element of the action to maintain public order and public safety. It is important to note that social networks play a significant role in organizing mass riots in the 21st century. In our country, the number of people who regularly use the Internet is constantly growing.
According to the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications, the number of Internet users in Russia increased by 2.5 million over the past year. At the end of last year, 62% of the population of our country used the possibilities of the World Wide Web. Today it is customary to distinguish the following types of approaches to the very process of preventive work: long-term, short-term and current (immediate). With a long-term approach, special attention is paid to establishing and maintaining normal relationships with the population. It is carried out by special structural units working directly with the population. Preventive operations, raids, operations to confiscate illegally stored weapons and drugs are being carried out.
Preventive conversations are being held with people who have previously been in the field of vision of law enforcement organizations. Short-term preventive work involves the implementation of operational measures in order to relieve the tension that arises among the population, which can lead to mass excesses. Within the framework of short-term preventive work, an important place is occupied by a skillfully organized and conducted collection of information, including the methods of operational-search work, as well as an analysis of all the information collected. All this also applies to the work of collecting information about impending mass statements or excesses that are already taking place.
Today, a full range of measures is needed, which is provided for both by Russian legislation and by the relevant plans to ensure order in society. Immediately when there is a danger of mass protests turning into acts of violence or a change in the peaceful nature of the course of actions, law enforcement officers can apply various preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of large-scale riots. Regime measures are being carried out, which are a set of actions of the Department of Internal Affairs to partially or completely restrict the movement of vehicles and pedestrians in a certain area of the territory, at a specific time.
Inspection of vehicles and participants in order to detect and seize items used as weapons in the fight in the event of riots. Restrictions on mass gatherings of citizens in public places can be temporary (at a specified time) or permanent (several days, weeks). Intensified patrolling by units of the patrol service, in the area of riots. At the same time, special attention should be paid to groups of young people who are in a state of intoxication and are active. Discreetly stop minor hooligan actions and immediately stop the facts of hooligan behavior and quickly check the signals of citizens about preparing, possible mass violations of public order and riots, and act quickly when seizing the instigators.
In the event of a conflict situation, a law enforcement officer is obliged to qualitatively assess this situation, assessing their degree and danger, taking immediate measures to eliminate misconduct at the beginning of the events, informing the police officer on duty about the nature of the conflict, time, place and reason for its occurrence or maturation, the contingent and the number of participants, the number of people, their direct relation to the incident, and individual subjects may be in a state of internal conflict over the choice of behavior in a particular situation. Often tactless, rude communication (treatment) of police officers with citizens in mass events is really capable of provoking riots. In the process of maintaining public order, there are often cases of illegal actions of law enforcement officers in relation to participants in mass events, which received a wide response in society.
The psychological measure of preventing mass riots is the ability of all employees of law enforcement organizations to resist provocations from the most aggressive participants in the event, which, first of all, should in fact be ensured by conducting special training sessions on psychology. Tactically competent actions of law enforcement organizations allow in certain cases to prevent the onset of riots, and in the conditions of riots that have begun, they allow them to perform their duty with minimal casualties. The study of domestic and international experience in combating riots, as well as an analysis of the practice of law enforcement organizations, is essential to improve preventive work in this direction.
Literature
1. Kuzmin Yu.A. Victimological prevention of crimes // Actual problems of legal science and law enforcement practice. Collection of materials of the VI International Scientific and Practical Conference dedicated to the 25th anniversary of the Faculty of Law. 2016. S. 370 - 374.
2. Levushin A.N. Modern humanism and environmentalism: conflict and interaction of two styles of thinking: dissertation abstract for the degree of candidate of philosophical sciences / Chuvash State University. I.N. Ulyanov. Cheboksary, 2010. 24 p.
3. Maslyuk I.A., Kuzmin Yu.A. Ensuring the safety of participants in criminal proceedings // Actual problems of legal science and law enforcement practice Collection of materials of the III International Scientific and Practical Conference. 2013. S. 339 - 342.
4. Salivarov V.Ya., Kuzmin Yu.A. Dispositiveness, as well as issues of termination of a criminal case and criminal prosecution in criminal proceedings // Actual problems of legal science and law enforcement practice, collection of materials of the 4th Intern. scientific - pract. conf. 2014. S. 440 - 444.
Yu.A. Kuzmin
Tags: Previous postNext post
To successfully ensure public safety in the prevention and suppression of riots, effective interaction between units, groups, and subunits is necessary. To ensure it, organized management is required.
The organization of the management of the forces and means of the internal affairs bodies in the prevention and suppression of riots is divided into three stages (see Appendix 21).
First (preliminary) stage includes the activities of the head (operational chief) for advance planning and preparation of command and all personnel for any type of special activity.
Second phase involves the activities of the leader (operational chief) in managing forces and means in preparing them for specific actions in the event of an emergency (for example, in the event of mass riots).
Third stage- the work of the head (operational chief) in managing forces and means in the course of their activities to restore public security in any conditions of the situation.
Let us consider these stages in more detail, taking into account some conventions and generalization of this activity of the leader (operational chief), regardless of the position held.
The organization of management of the special activities of the internal affairs bodies at the first (preliminary) stage is understood as a set of actions of the head for the preparation of planning documents and clarification of the initial data in the event of an emergency, at subsequent stages - a constant managerial impact on subordinates during the implementation of the plan.
The organization of management begins with the planning of special activities, on the basis of which the entire private and commanding staff of the ATS forces are trained.
Before starting planning special activities for the prevention and suppression of riots, the head of the Internal Affairs Directorate is obliged to carry out certain work to develop decisions on the expected (possible) actions of subordinates, depending on the conditions of the emergency. In this case, the decision is an algorithm of a possible course of action in a certain situation (what riots can occur, what actions need to be taken to prevent them).
Let us consider in general terms this work related to the process of developing a solution for planning special activities of the Internal Affairs Directorate of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, although this is also applicable to any city district authority. It should be noted that the decision is made by the head of the ATC, but the leadership of the ATC (headquarters of the combined ATC detachment) can take part in its development. At the same time, the final decision on all issues of planning the activities of forces and assets belongs only to the head of the ATC.
The work of the chief of the Internal Affairs Directorate and the operational headquarters of the combined detachment in developing a solution for planning the activities of forces and means to prevent and suppress mass riots is built in the following sequence: understanding the task, making the necessary calculations of time and forces, assessing the expected (possible) situation. If necessary, to calculate the forces and means at certain places of possible actions of the internal affairs bodies, they are reconnoitered (see Appendix 4).
As a result of this work, a decision is made on planning the special activities of the forces and means of the ATC as a whole (including the tactical actions of the combined ATC detachment), for special operations. Carry out work to clarify the upcoming tasks with possible actions of the Department of Internal Affairs. Determine the possible design of the planned special operations.
The ultimate goal of the special activity of the ATC forces and means is to ensure public safety. This can be achieved by carrying out individual measures, and if the operational situation becomes more complicated, by conducting a special operation with the participation of the forces of the combined ATC detachment, which is reflected in the plan.
In this regard, they set specific tasks for the detachments, groups and subunits for their actions at any stage of the development of events. On the plan (diagram) of the city or on demonstration diagrams of places where it may be necessary to use the forces and means of the internal affairs bodies, they determine the places of concentration, initial areas, deployment lines and initial lines, the lines for the start of actions for units, groups and orders. All tasks are specified already in the course of events. It must be borne in mind that forces and means must be ready to perform other tasks to ensure public safety.
The place of actions of the ATS forces depends on the development of events and the possible place of the outbreak of riots. Therefore, planning is carried out with respect to possible places of illegal actions, which are classified according to certain criteria and divided into several groups. For example, the first group consists of places that have a large area (squares, squares, parts of streets, etc.), the second group - places on the streets, avenues, street intersections; the third - places with a mass congestion of citizens (railway and river stations, bus station, airport, markets, etc.); the fourth - places of mass sports and cultural events (stadiums, sports palaces and other places of concentration of spectators); fifth - places limited by various buildings, small in area, with a small number of approaches and entrances; the sixth - the places of possible initial gatherings of the crowd for the subsequent movement to the intended objects (vacant lots, various sites).
After a thorough classification, the forces and means are calculated, as well as the time for their concentration for each group. To do this, a place is selected from each group with such a condition that it has most of the features characteristic of this group. On the basis of such a place, a calculation of forces and means is carried out for a special operation to suppress riots. When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the possible size of the crowd, as well as the actual number of forces and means of the combined ATC unit required to carry out all possible activities. In addition, it is far from always possible to collect all the planned forces and means of the combined ATC unit: employees can be on vacation, on treatment, on business trips, etc. Therefore, they calculate the average number of personnel, and then determine in reality how many employees should be allocated by each city district authority, units of the ATC apparatus, a special battalion, division, educational institutions and internal troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation.
The Department of Internal Affairs allocates 60% of the listed personnel, internal troops and educational institutions - 75% of the real number. It is advisable to plan the allocation of employees as part of units with their own commander.
When assessing the general situation, they take into account the alleged (possible) places of mass unrest, the operational situation, their forces and means, the terrain, the time of year and day, and weather conditions.
At assessment of alleged (possible) riots take into account: the general socio-economic situation in the region (city), the presence of acute social conflicts, which can involve a large number of citizens, and the procedure for their resolution; causes and conditions that may contribute to the emergence of riots; the presence of educational institutions, hostels, the private sector, self-construction, the social composition of the population (workers, employees, students, schoolchildren), employment of the population (in state, private production, etc.) (see Appendix 5).
When assessing the general situation take special account of the operational situation and the prospects for its development; the state of crime and its types; the prevalence of violent crime and the trend towards an increase in their number; the number and place of residence of conditionally convicted and released on parole, previously convicted for dangerous violent crimes, repeatedly convicted (recidivists) for hooliganism, robbery, robbery and other intentional crimes; the presence of unemployed and unwilling to work criminal groups; the presence of persons prone to the distribution of drugs, false rumors, including informal organizations; the existence of population groups hostile to the new economic changes; the presence of objects on which criminal encroachments can be directed, etc.
At assessing one's strengths proceed from their number, degree of training, experience in similar actions, availability of special equipment and equipment. They make a conclusion about their ability to restore law and order, to apply the necessary measures in a timely manner, to properly organize and specialize personnel. The readiness of forces and means is checked at ongoing command-staff and general exercises.
The main conclusion from the assessment of the situation when planning special activities, it must be unambiguous whether the forces and means of the ATC are capable of performing the task in any area of the city, in any calculated place. If this is not possible, then the causes are determined and work is carried out to eliminate them. This may be the unpreparedness of the personnel, their poor equipment, the lack of a sufficient amount of transport and people (in this case, they are looking for the possibility of attracting regional forces and means).
To prevent riots, special measures are planned: operational, investigative, explanatory, preventive, organizational, social, etc.
In some cases, regime events and individual military (tactical) actions are carried out, for example, cordoning off an area (place) of possible unrest, enhanced patrolling.
To suppress the riots, they plan to carry out complex military (tactical) actions to block the crowd and disperse it.
When planning special activities, the time of year is taken into account. From here, the uniform and additional uniforms for the personnel involved are determined. For example, to serve in the winter, it is advisable to put personnel (patrol outfits, cordons, blocking, scattering) in jackets, felt boots, sheepskin coats, pea coats. The HOZO food service provides the personnel with hot tea. In cold weather, places for heating personnel are prepared (for example, in buses). In summer, depending on the weather, the uniform should be extremely lightweight so that it does not restrict movement. At temperatures above 25 degrees, a field uniform is appropriate. For example, when planning a riot control operation using shields, in order not to injure each other and to mitigate the impact, employees prepare special pads for the arm supporting the shield. To protect the legs, it is advisable to purchase shields in advance.
At night, personnel must have lights (patrol group, cordon group, movement restrictions, blocking, protection of important objects, use of technical and special means).
Thus, planning is an integral part of the organization of management of internal affairs bodies to ensure public safety in an emergency. Early action for the general preparation of the command and all personnel of the internal affairs bodies for special activities to prevent and suppress mass riots is an important management element.
The main stages of the emergence and development of a conflict situation can be divided into three stages:
1. First stage characterized by the appearance of an occasion, which, as a rule, is some kind of emergency event. During this period, various rumors of a provocative nature appear and spread. Groups of people begin to form, from which a crowd can subsequently form.
The crowd usually does not gather by itself, there are always people who can be called organizers. They, using rumors, speculation, some facts, actively influence the emotional excitement of the audience, thereby pushing the crowd to illegal actions. Often, the organizers are the informal leaders of individual groups, they know how to convince and turn on the crowd. In addition to the organizers in the crowd, as a rule, there are instigators and provocateurs who, using the emotional state of the crowd, with the help of false rumors and misinformation, try to provoke the unorganized mass of the people into illegal actions.
Often, groups of the most aggressive-minded individuals are formed in the crowd, with the goal of committing crimes and other dangerous acts in an atmosphere of general confusion. They most often become the leaders, the first to start pogroms, arson and beatings of representatives of power and administration, they are usually called executors. Often these are antisocial elements and former criminals. The bulk of the crowd is made up of those who are mistaken in assessing the causes and causes of the conflict and are simply curious citizens who, in the end, can become not only participants in mass riots, but also their victims, which most often happens in practice.
2. active stage– the crowd turns to purposeful illegal actions, which are accompanied by pogroms, arson, robberies; other acts of violence are committed, traffic is blocked, barricades are erected, there is active resistance to representatives of the authorities, including with the use of various types of weapons.
3. The final stage- is characterized by the localization and elimination of the conflict through the active participation of law enforcement agencies in the suppression and elimination of group violations of public order, riots, in identifying those responsible for their organization, pogroms, robberies and destruction, and bringing these people to justice. The most difficult but necessary task is to identify at this stage the organizers, instigators, perpetrators, to fully and objectively document their illegal activities so that innocent citizens do not suffer.
Due to the fact that group violations of public order, mass riots arise, as a rule, spontaneously, have a rapid spread, are accompanied by the commission of serious crimes and a significant number of the population can participate in them, the internal affairs bodies must be in constant readiness to suppress and eliminate such antisocial actions. In accordance with the regulations of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, special operations are being developed in the internal affairs bodies to carry out security measures during this period.
Organizational events to ensure the preparation, organization, management of forces and means involved in the implementation of tasks to prevent and suppress group violations of public order, mass riots, is carried out by an operational headquarters specially created for this.
The main functions of the headquarters are:
1. Organization of prevention of riots:
Collection, generalization and evaluation of data on the operational situation, forecasting and development of specific scenarios for its development;
Development and organization of preventive measures, using the capabilities of the media, public formations in working with the population, labor collectives to prevent mass riots;
Informing the state authorities and administration about the increase in social tension, interethnic contradictions, their possible consequences, making proposals to eliminate the causes and conditions that contribute to the aggravation of the situation, assisting them in the implementation of proposals that fall within the competence of the internal affairs bodies;
Setting tasks for the localization of group antisocial manifestations and the prevention of riots, control and assistance in their implementation.
2. Ensuring the readiness of forces and means for action during mass riots.
3. Management of forces and means in the suppression of riots:
Notification and collection of members of the operational headquarters and personnel according to established signals, issuance of weapons, special equipment, communications equipment, alerting vehicles;
Collection and analysis of information about the current situation, its generalization and report to the head of the operational headquarters, making proposals for organizing the suppression of riots;
Preparation of calculations for the placement, promotion and deployment of a grouping of forces and means;
Deciding on the suppression of riots, setting tasks for the use of forces and means involved, organizing their interaction;
Monitoring the fulfillment of the assigned tasks by this group and providing the necessary assistance in their solution;
Keeping a log of actions in the operation, maps (schemes) and other operational and service documentation.
4. Organization of work to eliminate the consequences of mass riots:
Blocking the area of the operation and ensuring the protection of especially important facilities for the period of liquidation of the consequences of mass riots;
Gathering personnel, checking its availability, providing medical assistance to the victims;
Creation of mobile operational groups to prevent the re-collection of rioters;
Organization of public order protection by patrol groups according to the enhanced version;
Traffic regulation;
Firefighting and emergency rescue operations;
Elimination of the threat of explosions;
Logistic support;
Logistics;
Medical support;
Reserve - is created to perform tasks that suddenly arise during the operation. The size of the reserve, its weapons and equipment are determined by the head of the operational headquarters, depending on the prevailing situation.
General goals operations are:
Protection of life and health of people;
Prevention (reduction) of damage to state, public, personal (private) property;
Prevention and suppression of offenses and crimes, identification of the perpetrators, their neutralization and prosecution.
TO forces involved in the special operation include:
Personnel of bodies and institutions of internal affairs;
Personnel of combat police units;
Students and cadets of higher and secondary educational institutions of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia;
Servicemen of the internal troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, who act both jointly with employees of the internal affairs bodies under a single leadership, and independently.
TO funds used in special operations include:
Weapons and special means;
Operational, forensic and special equipment;
Means of communication;
motor vehicles;
Service dogs;
Combat and special equipment, special means and means of engineering weapons of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia.