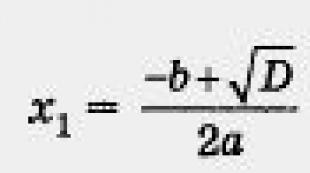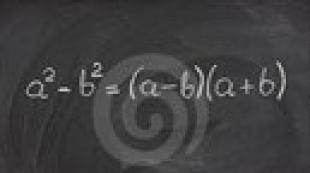Types of speech. What is a type of speech? What type of speech is represented by the sentence
Instruction
Start style definitions by specifying the scope of the text and its main functions. Scientific style in scientific textbooks, lectures, reviews, etc. These contain information about the phenomena around us and "submit" the material from a scientific point of view. Official business style is used in the field of legal relations, office, industrial, diplomatic. Its main function is information, . It is distinguished by the stereotyped construction of the text when writing various documents, charters, instructions, etc. Journalistic style is the style of newspapers, speeches on current socio-political topics. In the works of journalism, two goals are usually set: informing about certain social phenomena and at the same time actively influencing the reader or listener. Artistic style in works of fiction and is intended to create images and emotional and aesthetic impact on the reader. Conversational style is the style of live conversational speech, i.e. its main function is to ensure communication between native speakers. In writing, it exists in works of art to convey dialogue and create a character's speech characteristics.
When determining the style of text, consider its language features. Scientific texts are saturated with special vocabulary, terms, words are almost always used in their direct meaning in order to avoid ambiguity in their interpretation. There are a lot of words and combinations in official business style documents, which are called clericalisms and give the texts a prescriptive character, for example: it is necessary to urgently prepare, after the expiration of the term, it is not subject to appeal, to consider in the prescribed manner, etc. In the vocabulary of the journalistic style, there are many turns of a socio-political nature, exclamatory and incentive sentences are used in the syntax. A characteristic language device of the artistic style is the widespread use of words in a figurative sense to create an image and emotionally evaluative words to express the author's position. In colloquial style, colloquial and colloquial vocabulary and constructions of incomplete sentences are used in large quantities.
When determining the type of speech, consider how the content of the utterance is "served". If the text tells about the events taking place, the actions following one after another - this is a narrative. Descriptive texts talk about the simultaneity of the manifestation of signs of objects, phenomena or actions. Reasoning is characterized by the presence of a statement (thesis), which should be proved, and an argumentation base with actual examples.
Every child learning Russian knows the difference between a text and a simple set of sentences.
Text features
The text is sentences interconnected. They are connected by meaning, integrity. Only the text can have a certain structure, in which all sentences serve one common thought. Distinguish between oral and written text. A single sentence cannot be considered a coherent text. There must be at least two of them. The idea and theme make up the meaning of all the sentences put together. Each text has its own compositional structure, which includes the traditional three parts: introduction, main part and conclusion. The main idea, the theme of the text, the problems are revealed in the first part. The main part contains the development of events.
To move on to the question of types of text, it is first worth saying a few words about styles of speech. There are two of them: colloquial and book. The second has several subspecies:
- scientific,
- journalistic,
- official business
- art.
Text types
There are three main types of texts:
- storytelling,
- description,
- reasoning.
« Narration”is a story about events connected sequentially in time. A distinctive feature of the narrative is manifested in the structure: the plot of events, their development and denouement. The story is told in third person and first person. Verbs are used in the perfect form of the past tense.
Type of " description"has a consistent description and image of objects, events, people. There is an enumeration of properties and characteristics that belong to the described character. The description may contain sentences with homogeneous definitions, additions and circumstances. Metaphors, comparisons, epithets and other means of language expressiveness are used. The main task of this type of text is to create an idea about the described subject.
Text type " reasoning"contains the study and study of individual subjects, their connection with each other is revealed. In reasoning there is a certain scheme and a logically well-built structure. The introduction contains the main idea, an assumption is made or a thesis is formulated. Vivid evidence and arguments are given as confirmation or refutation. Conclusions are contained at the end of the text.
Types of speech are varieties of language depending on what we want to convey in the text: tell, depict or prove something.
There are three types of speech: narrative, description, reasoning. As a rule, types of speech are rare in their pure form, usually they are combined.
So, for example, a narrative may include elements of description, or a description may include elements of reasoning.
Narration
To the texts of the narrative, you can ask the question what happened?
The purpose of narrative texts is to tell about an event, a fact of reality. Narrative texts reflect several episodes, events connected with each other.
Narrative texts are built according to the following scheme: exposition, plot, development of action, climax, denouement. One of the characteristics of storytelling is dynamism. The leading part of speech is a verb, which allows you to convey the dynamics, as well as special words with the meaning of time (first, then, then, in the morning, in the evening, etc.).
The narrative is based on the unity of the types of the temporal plan, that is, the verbs must be in the same tense and be of the same type. Narrative is usually used in texts of artistic or colloquial styles.
Description
For description tests, you can ask what (what) subject?
The purpose of description tests is to describe items. An image of an object or a description of a phenomenon is created by listing its features. The description object is static, there are no dynamics in the description.
The compositional scheme of the description text is the following: beginning, main part, ending. At the beginning, as a rule, the subject of the description is called, then the signs of the subject are listed, on the basis of which a complete image of the subject of the description is formed, at the end a conclusion is made - a general assessment of the subject.
Signs of an object are conveyed by adjectives, participles or verbs-predicates. Just like the narrative, the unity of the types of the temporal plan is important in the description. As a rule, simple sentences are used in the description, although often complex sentences are used.
The description is used in texts of any style.
reasoning
To tests of reasoning, you can ask the question why? The purpose of description tests is the assertion or denial of any fact, phenomenon, concept, in addition, reasoning texts reveal cause-and-effect relationships between phenomena.
Reasoning texts are built according to the following scheme: thesis, arguments, conclusion. The thesis is the main idea that is proved in the text, the arguments are the evidence with which the thesis is proved, the conclusion is the result of reflection.
Reasoning texts can be divided into reasoning-proof (why?), reasoning-explanation (what is it?), reasoning-thinking (how to be?). In reasoning, any vocabulary is used; for reasoning, the unity of the species-temporal plan is not important. Reasoning is used in texts of any style.
Types of figurative and expressive means
Tropes (based on the lexical meaning of the word)
Epithet- a word that defines an object or phenomenon and emphasizes any of its properties, qualities, signs. Usually an epithet is called a colorful definition:
Your thoughtful nights transparent dusk (A. S. Pushkin).
Metaphor- a trope in which words and expressions are used in a figurative sense based on analogy, similarity, comparison:
And my tired soul is embraced by darkness and cold (M. Yu. Lermontov).
Comparison- a trope in which one phenomenon or concept is explained by comparing it with another. Comparative conjunctions are usually used in this case:
Anchar, like a formidable sentry, stands alone - in the whole universe (A. S. Pushkin).
Metonymy- Trope, based on the replacement of one word by another, adjacent in meaning. In metonymy, a phenomenon or object is denoted with the help of other words or concepts, while their connections and features are preserved:
The hiss of frothy glasses and the blue flame punch (A. S. Pushkin).
Synecdoche- one of the types of metonymy, which is based on the transfer of meaning from one object to another on the basis of the quantitative relationship between them:
And it was heard before dawn how the Frenchman rejoiced (meaning the entire French army) (M. Yu. Lermontov).
Hyperbola- a trope based on the excessive exaggeration of certain properties of the depicted object or phenomenon:
For a week I won’t say a word to anyone, I’m all sitting on a stone by the sea (A. Akhmatova).
Litotes- trope opposite of hyperbole, artistic understatement:
Your Spitz, lovely Spitz, is no more than a thimble (A. Griboyedov).
personification- trope, which is based on the transfer of the properties of animate objects to inanimate ones:
Silent sadness will be consoled, and joy will reflect friskyly (A. S. Pushkin).
Allegory- trope based on the replacement of an abstract concept or phenomenon with a specific image of an object or phenomenon of reality:
Medicine is a snake wrapped around a bowl, cunning is a fox, etc.
paraphrase- a trope in which the direct name of an object, person, phenomenon is replaced by a descriptive expression, which indicates the signs of an object, person, phenomenon not directly named:
The king of animals is the lion.
Irony- a technique of ridicule, containing an assessment of what is ridiculed. In irony there is always a double meaning, where the true is not directly stated, but implied:
Count Khvostov, a poet beloved by heaven, was already singing with immortal verses of the misfortune of the Neva banks (A. S. Pushkin).
Stylistic figures
They are based on a special syntactic construction of speech.
Rhetorical address- giving the author's intonation solemnity, pathos, irony, etc.:
Oh, you haughty descendants... (M. Yu. Lermontov).
Rhetorical question- such a construction of speech in which the statement is expressed in the form of a question. The rhetorical question does not require an answer, but only enhances the emotionality of the statement:
And over the fatherland of enlightened freedom will a beautiful dawn rise at last? (A. S. Pushkin)
Anaphora- repetition of parts relative to independent segments, otherwise anaphora is called monophony:
As if you curse the days without a light, as if the gloomy nights scare you (A. Apukhtin).
Epiphora- repetition at the end of a phrase, sentence, line, stanza.
Antithesis- a stylistic figure based on the opposition:
And day and hour, both in writing and orally, for the truth yes and no ... (M. Tsvetaeva).
Oxymoron- connection of logically incompatible concepts:
Living corpse, dead souls, etc.
gradation- grouping homogeneous members of a sentence in a certain order: according to the principle of increasing or weakening emotional and semantic significance:
I do not regret, do not call, do not cry. (S. Yesenin)
Default- intentional interruption of speech, based on the guess of the reader, who must mentally finish the phrase:
But listen: if I owe you ... I own a dagger, I was born near the Caucasus. (A. S. Pushkin)
Nominative topics (nominative representations)- a word in the nominative case or a phrase with the main word in the nominative case, which is at the beginning of a paragraph or text and in which the topic of further reasoning is stated (the name of the subject is given, which serves as the topic of further reasoning):
Letters. Who likes to write them?
Parceling- intentional splitting of one simple or complex sentence into several separate sentences in order to draw the reader's attention to the selected segment, to give it (the segment) additional meaning:
The same experience has to be repeated many times. And with great care.
Syntax parallelism- the same construction of two or more sentences, lines, stanzas, parts of the text:
The stars are shining in the blue sky
Waves crash in the blue sea.
(sentences are built according to the scheme: adverb of place with a definition, subject, predicate)
A cloud is moving across the sky, A barrel is floating on the sea. (A. S. Pushkin)
(sentences are built according to the scheme: subject, circumstance of place, predicate)
Inversion- violation of the generally accepted grammatical sequence of speech:
The sail of the lonely one turns white in the blue mist of the sea. (M. Yu. Lermontov)
(according to the rules of the Russian language: A lonely sail turns white in the blue fog of the sea.)
Means of communication of sentences in the text
Lexical means:
- Lexical repetition- repetition of a word or the use of a single-root word. For scientific and official texts, the repetition of a word is the main means of communication. Quite often used in the description.
- Synonymous replacement- replacing a word in one of the sentences with a synonym or a synonymous expression in another. It is usually used where colorfulness of speech, its figurativeness, expressiveness is needed - journalistic, artistic styles.
- The two sentences may be related generic relations: genus as a broader concept, species as a narrower one.
There are many trees in this forest. But first of all, you notice the trunks of your favorite birches. - Use of antonyms.
- The use of words of one thematic group.
There are many Karamazovs in Russian life, but still they do not direct the ship's course. Sailors are important, but even more important for the captain and the sailboat is the tiller and the star, on which the ideal is oriented.
The school curriculum necessarily has a theme: "Types of speech: description, narration, reasoning." But after a while, knowledge tends to be erased from memory, so it would be useful to fix this important issue.
What are types of speech? What functions do they perform?
Types of speech: description, narration, reasoning - this is how we talk about a subject. For example, imagine an ordinary table in the office or at home in the kitchen. If you need to describe this item, then you should tell in detail how it looks, what is on it. Such text will be descriptive, therefore, it is a description. If the narrator begins to talk about what this table is for, is it too old, is it not time to change it to a new one, then the chosen type of speech will be called reasoning. A text can be called a narrative if a person tells the story of how this table was ordered or made, brought home and other details of the appearance of the table on the territory of the apartment.
Now for some theory. Types of speech are used by the narrator (author, journalist, teacher, announcer) to convey information. Depending on how it is presented, the typology is determined.
Description is a type of speech, the purpose of which is a detailed story about a static object, image, phenomenon or person.
The narrative informs about the developing action, conveying certain information in a temporal sequence.
With the help of reasoning, the flow of thought regarding the object that caused it is transmitted.
Functional-semantic types of speech: description, narration, reasoning
Types of speech are often called functional-semantic. What does it mean? One of the meanings of the word "function" (there are many others, including mathematical terms) is a role. That is, speech types play a role.
The function of description as a type of speech is to recreate a verbal picture, to help the reader see it with his inner vision. This is achieved through the use of adjectives in various degrees of comparison, adverbial phrases, and other speech means. This type of speech is most often found in artistic style. A description in a scientific style will differ significantly from an artistic one in the unemotional, clear course of the story, the obligatory presence of terms and
Narrative is characterized by an image of an action, a situation or a specific case. Using verbs and short, concise sentences, this type of speech is often used in news reports. Its function is notification.
Reasoning as a type of speech is characterized by a variety of styles: artistic, scientific, business and even colloquial. The pursued goal is to explain, reveal certain features, prove or disprove something.
Features of the structure of speech types
Each type of speech has a distinct structure. The narrative is characterized by the following classical form:
- string;
- development of events;
- climax;
- denouement.
The description does not have a clear structure, but it differs in such forms as:
- a descriptive story about a person or animal, as well as an object;
- a detailed description of the place;
- state description.
Similar examples are often found in literary texts.
Reasoning is fundamentally different from previous types of speech. Since its purpose is to convey the sequence of the human thought process, the reasoning is constructed as follows:
- thesis (statement);
- arguments, together with given examples (proof of this statement);
- final conclusion or conclusion.
Often types of speech are confused with styles. This is a gross mistake. Below we will explain how styles differ from types.

Types and styles of speech: what are the differences?
The concept appears in Russian language textbooks What is it and are there any differences between styles and types?
So, style is a complex of certain speech means used in a particular area of communication. There are five main styles:
- Colloquial.
- Publicistic.
- Official business (or business).
- Scientific.
- Art.
To see you can take any text. The type of speech which will be presented) is present both in scientific and journalistic style. we choose for daily communication. It is characterized by the presence of vernacular expressions, abbreviations and even slang words. It is appropriate at home or with friends, but upon arrival at an official institution, for example, a school, university or ministry, the style of speech changes to business with scientific elements.
Newspapers and magazines are written in a journalistic style. Using it, broadcast news channels. The scientific style can be found in the educational literature, it is characterized by many terms and concepts.
Finally, the art style. He wrote books that we read for our own pleasure. Comparisons (“the morning is beautiful, like the smile of a loved one”), metaphors (“the night sky pours gold on us”) and other artistic expressions are inherent in it. By the way, description is a type of speech that is quite common in fiction and, accordingly, in the style of the same name.
The difference is this: you can describe, reflect or narrate using different styles. For example, when talking about a flower in an artistic style, the author uses a lot of expressive epithets to convey to the listener or reader the beauty of the plant. A biologist, on the other hand, will describe a flower, from the point of view of science, using generally accepted terminology. In the same way, one can argue and narrate. For example, a publicist will write a feuilleton about a carelessly picked flower, using reasoning as a type of speech. At the same time, the girl, using a conversational style, will tell her friend how a classmate gave her a bouquet.
Using Styles
The specificity of speech styles makes their successful neighborhood possible. For example, if the type of speech is description, then it can be supplemented with reasoning. All the same flower can be described in the school wall newspaper, using both scientific or journalistic, and artistic style. It can be an article about the valuable properties of a plant and a poem praising its beauty. In a biology lesson, the teacher, using a scientific style, will offer students information about a flower, and after that he can tell a fascinating legend about it.

Type of speech description. Examples in literature
This type can be conditionally called an image. That is, when describing, the author depicts an object (for example, a table), natural phenomena (thunderstorm, rainbow), a person (a girl from a neighboring class or a favorite actor), an animal, and so on ad infinitum.
As part of the description, the following forms are distinguished:
Portrait;
Description of the state;
Examples of the landscape, you can find in the works of the classics. For example, in the story "The Fate of a Man" the author gives a brief description of the early post-war spring. The pictures recreated by him are so alive and believable that it seems that the reader sees them.

In Turgenev's story "Bezhin Meadow" landscapes also play an important role. With the help of the verbal image of the summer sky and sunset, the writer conveys the powerful beauty and strength of nature.
To remember what a description is as a type of speech, it is worth considering another example.
“We went on a picnic outside the city. But today the sky was gloomy and became more and more unfriendly towards evening. At first the clouds were of a heavy gray hue. The sky was covered with them, like a theater stage after a performance. The sun had not yet set, but it was already invisible. And now lightning appeared between the gloomy curtains of the clouds ... ".
The description is characterized by the use of adjectives. It is thanks to them that this text gives the impression of a picture, conveys color and weather gradations to us. The following questions are asked for a descriptive type story: “What does the described object (person, place) look like? What signs does he have?

Narration: an example
Discussing the previous type of speech (description), it can be noted that it is used by the author to recreate the visual effect. But the narrative conveys the plot in dynamics. This speech type describes events. The following example tells about what happened to the heroes of a short story about a thunderstorm and a picnic next.
“... The first lightning did not frighten us, but we knew that this was only the beginning. We had to collect our things and run away. As soon as a simple dinner was packed into backpacks, the first drops of rain fell on the bedspread. We rushed to the bus stop."
In the text, you need to pay attention to the number of verbs: they create the effect of action. It is the image of the situation in the time period that is the hallmark of the narrative type of speech. In addition, questions of this kind can be asked to a text of this kind: “What was first? What happened next?

Reasoning. Example
What is reasoning as a type of speech? Description and narration are already familiar to us and are easier to understand than text-reasoning. Let's go back to friends caught in the rain. One can easily imagine how they are discussing their adventure: “… Yes, we were lucky that the summer resident motorist noticed us at the bus stop. Good thing he didn't pass by. In a warm bed it is good to talk about a thunderstorm. Not so scary if we were at the same stop again. A thunderstorm is not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. You can't predict where lightning will strike. No, we will never go out of town again without knowing the exact weather forecast. A picnic is good for a sunny day, but in a thunderstorm it’s better to drink tea at home.” The text contains all the structural parts of reasoning as a type of speech. In addition, you can ask him questions that are characteristic of reasoning: “What is the reason? What follows from this?

Finally
Our article was devoted to the types of speech - description, narration and reasoning. The choice of a particular speech type depends on what we are talking about in this case and what goal we are pursuing. We also mentioned the characteristic speech styles, their features and close relationship with the types of speech.
10 Read the fragment of the dictionary entry, which gives the meaning of the word "served". Determine the meaning in which this word is used in the eighth (8) sentence of the text. Write down the number corresponding to this value in the given fragment of the dictionary entry.
CJI UZHI "TH, I serve, you serve; nesov.
1. Carry, perform service (in 2, 3 and 6 meanings) Serve in the ministry. To serve in the military. Serve Mass.
2. trans., to someone. To do something for someone (something), fulfilling someone's will, orders, direct one's activity for the benefit of something (high). Serve your people. Serve art.
3. how. To have something for one's purpose; to be fit for something. The sofa serves as a bed. Serve as an example. Serves as evidence.
4. (1st and 2nd person not used). Fulfill your assignment. The old suit is still in service.
5. About dogs: stand on their hind legs . Serve the ball!
6. Happy to serve (official) - a polite expression of readiness to render a service.
11 In which sentence is a metaphor used as a means of speech expressiveness? Write the number of this offer.
(27) The sprouts of love for native nature in a young soul sprouted in early childhood.
(8) Special pride is the simple things that served Turgenev: a gun, a hat, a bag for game, a powder flask, a flask for water, a cane that he used while walking.
(24) Ivan was not interested in expensive toys.
(11) The number of current guests here is measured in thousands.
Answer: ________________________________________
12 From sentence 28, write out the subordinating phrase with the connection CONNECTION.
Answer: ________________________________________
13 You write grammatical basis suggestions 9.
Answer: ________________________________________
14 Among sentences 19-23 find simple one-part indefinite personal sentence
Answer: ________________________________________
15 Install conformity between sentences taken from the text and their syntactic characteristics: for each element of the first column, select an element of the second column.
|
SUGGESTIONS |
SYNTAX CHARACTERISTIC |
|
A) Observing the interests of her son, the mother ordered to hang cages with siskins, tits, and goldfinches everywhere. |
1) A simple sentence complicated by an introductory word. |
|
2) A simple sentence complicated by a separate circumstance and homogeneous members. |
|
|
B) Here, in Spasskoye, he returned to breathe his native air, to meet friends. |
|
|
3) A simple sentence, complicated by a separate definition and homogeneous members. |
|
|
C) In the estate, which combined true Russian hospitality with European comfort, the writer's guests at various times were Tolstoy, Nekrasov, Fet, Shchepkin, Polonsky, Grigorovich, Savina, Uspensky, Garshin. |
|
|
4) A simple sentence complicated by a clarifying circumstance of place and homogeneous members. |
16 Among sentences 1-5, find one that connects with the previous ones using definitive pronoun. Write the number of this offer.
Answer: ________________________________________